The giant black holes that lurk in the hearts of galaxies appear to be much larger than we expect.
The central black holes in dwarf galaxies — the “seeds” that ultimately sprout into monsters in the center of the Milky Way and other large galaxies — are probably unusually heavy and have a weight of 10,000 times our Sun, reports a new study.
A new theory of the evolution of a supermassive black hole suggests that galaxies do not need merging to create these giants.
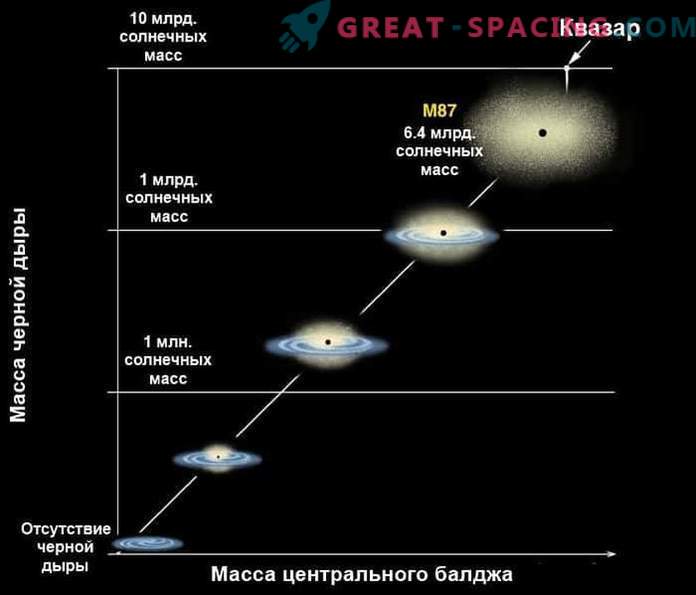
Dependence between the mass of a black hole and the mass of a bulge
"We still do not know how such monstrous black holes are formed that are located in the centers of galaxies," said lead author Shobita Satyapal, from George Mason University in Virginia. But the huge black holes found in tiny galaxies show us that black holes were born in the early Universe, before the time when the galaxies collided with each other. "
There is a possibility that supermassive black holes grow mainly due to the absorption of dust and gas, becoming more and more relatively gradually growing host galaxy, the researchers say.
Satyapal and her colleagues analyzed observations of dwarf galaxies made with the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (abbreviated as WISE) mounted aboard NASA spacecraft.
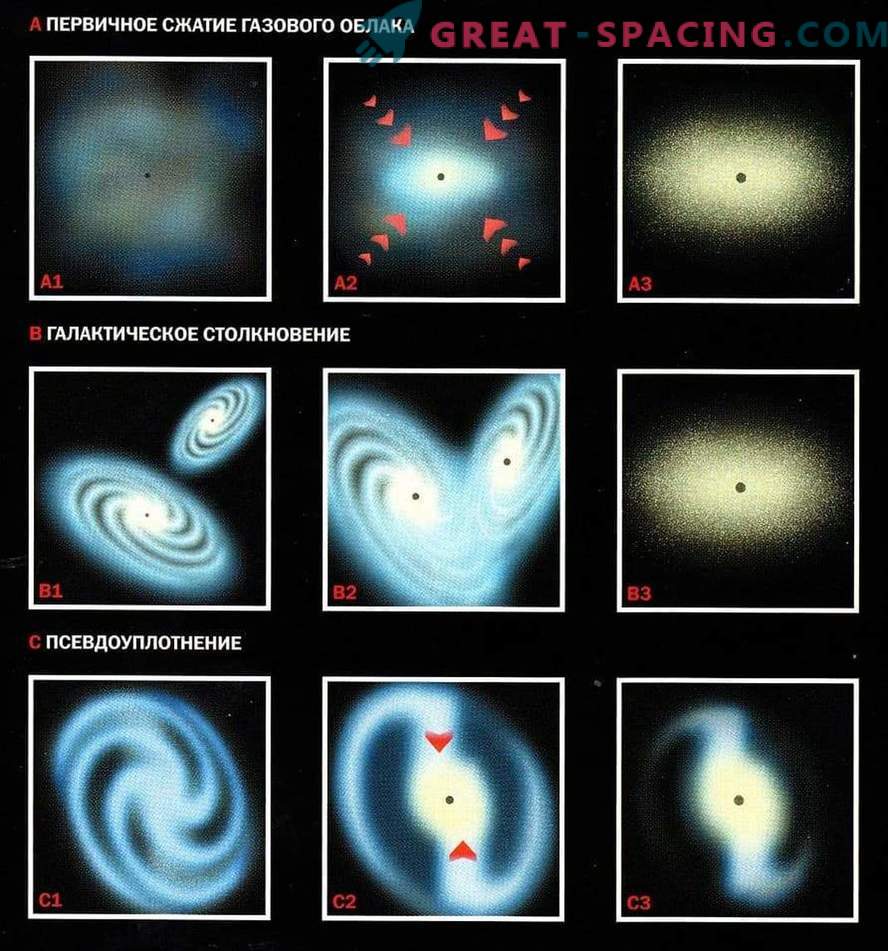
Growth of black holes
Dwarf galaxies change slightly and resemble the types of galaxies that existed when the universe was young. So they are a good place to look for nascent supermassive black holes, the researchers say.
In search of suitable candidates in the night sky, WISE selected hundreds of dwarf galaxies, which are potential sites for the birth of supermassive black holes.
“Our results show that proto-supermassive black holes are quite massive in their own right,” says Satyapal.
Although the results are intriguing, subsequent research is needed to completely fill all gaps in the knowledge about these objects, the researchers say.
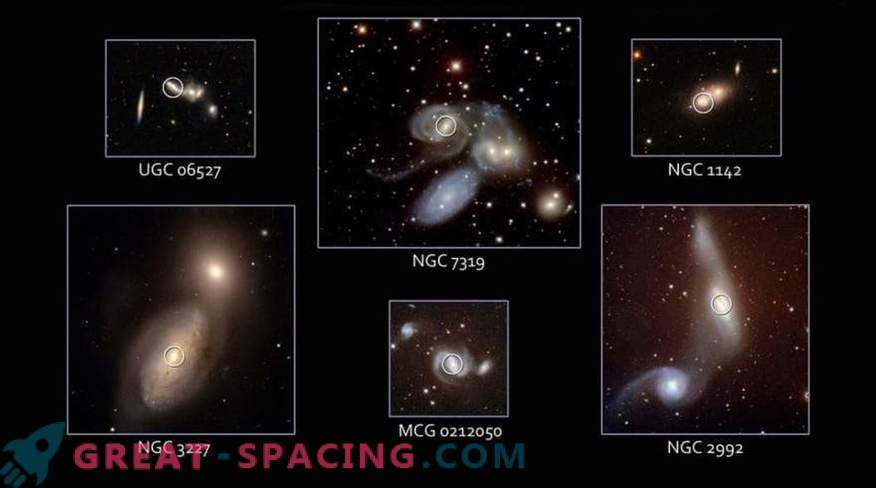

Black holes in merging galaxies
WISE was sent into orbit in December 2009 for a 10-month mission to scan the sky in infrared light. The project was closed in February 2011, and then resumed in September 2013 with a new mission and a new name. Now it is called Neowise. The spacecraft is used to search for potentially dangerous asteroids, some of which could be promising objects for human exploration.
A new study was published in the March issue of The Astrophysical Journal.