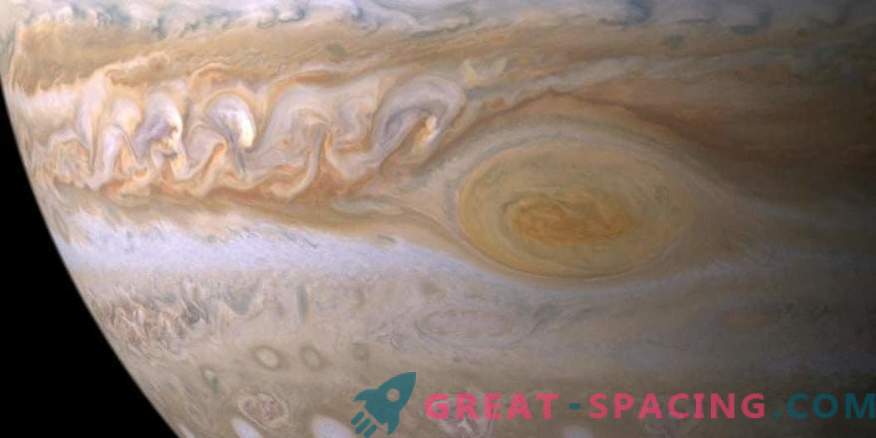
Here is a small part of the global map of Jupiter, made from observations of the Hubble Space Telescope
The size of the red spot of Jupiter is enough to absorb three of the Earth. However, scientists have noticed that over the past half century, its size has been reduced. No one was sure how long this feature of the gas giant would last.
New research suggests that due to compression the stain is getting higher. Storms are dynamic and the Jupiter blot confirms this. It is constantly changing in size and shape, and also shifts its winds. Researchers are lucky because this feature has been monitored for centuries.
The first entry on the Big Red Spot dates back to 1831. Scientists have long measured size and drift, so the data archive allowed us to combine information with the parameters of the two 1979 Voyager missions, as well as the Hubble telescope. This helped to trace the evolution of the Big Red Spot, analyzing in detail its size, shape, color and speed of movement. They also tracked the speed of the internal wind.
New data shows that the spot has recently begun to drift westward faster than before. The storm still remains at the same height, but rotates in the opposite direction. Historically, it was believed that the drift was constant, but now they record accelerated stretching.
It was believed that the Big Red Spot shrinks over time. Recent observations say that it is compressed, but becomes higher
Scientists confirm that the storm has decreased in length since 1878, but in the 1920s. growth temporarily activated. Because of the reduction, it was expected that powerful internal winds should become even stronger. But the storm began to pull out. Of course, the change is not very noticeable, but it can be noticed.
The stain color is also increasing, becoming more orange since 2014. Scientists are not sure why this is happening. It is possible that chemicals are transferred to the atmosphere during the process of stretching the stain. At high altitudes, substances will be exposed to greater UV radiation and will acquire blue hues.
If the observed trends continue for 5-10 years, we will get interesting results of the dynamics. Most likely, it will no longer hit with its gigantic size.