A week ago, the Aeolus satellite first activated in the atmosphere and now surpasses all expectations, demonstrating the first wind information. The satellite did not even remain in orbit for a month, but its indicators look extremely promising, which was not expected at the early stage of the mission. The information is displayed by ECMWF from one of the orbits.
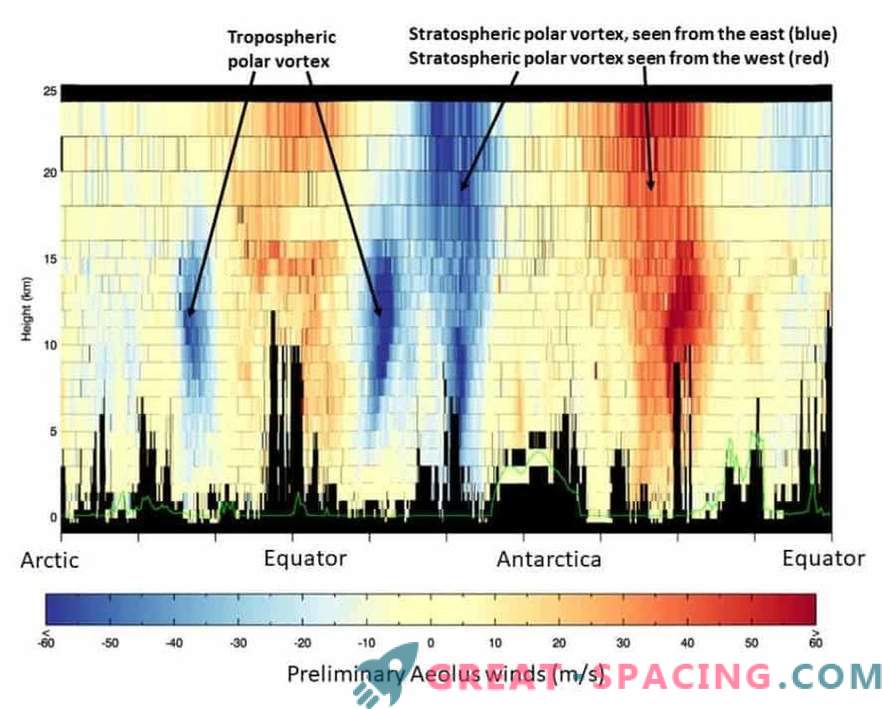
First wind data from ESA Aeolus satellite. Before you are the figures for 3/4 of the earth's orbit. Large-scale east and west winds are visible between the earth’s surface and the lower stratosphere, including jet streams. The satellite moves from the Arctic to the Antarctic, therefore it catches powerful currents of the westerly winds (tropospheric eddies - blue) from each side of the equator at middle latitudes. Moving further towards the Antarctic, it captures strong westerly winds
The profile shows large-scale east and west winds between the earth’s surface and the lower stratosphere, including jet streams. In addition, the stratospheric polar vortex around the South Pole is noticeable. These winds play an important role in the process of depletion of the ozone layer at this time of year.

Air movement is the general circulation of the atmosphere, transporting heat from equatorial regions to the poles and returning cooler air to the tropics. Atmospheric circulation in each hemisphere consists of three cells: Hadley, Ferrel and polar Aeolus is the fifth ESA mission that studies the most relevant scientific questions about the Earth. It uses a unique instrument that measures the wind from space. This is a revolutionary laser technology that allows direct global measurements of the wind.
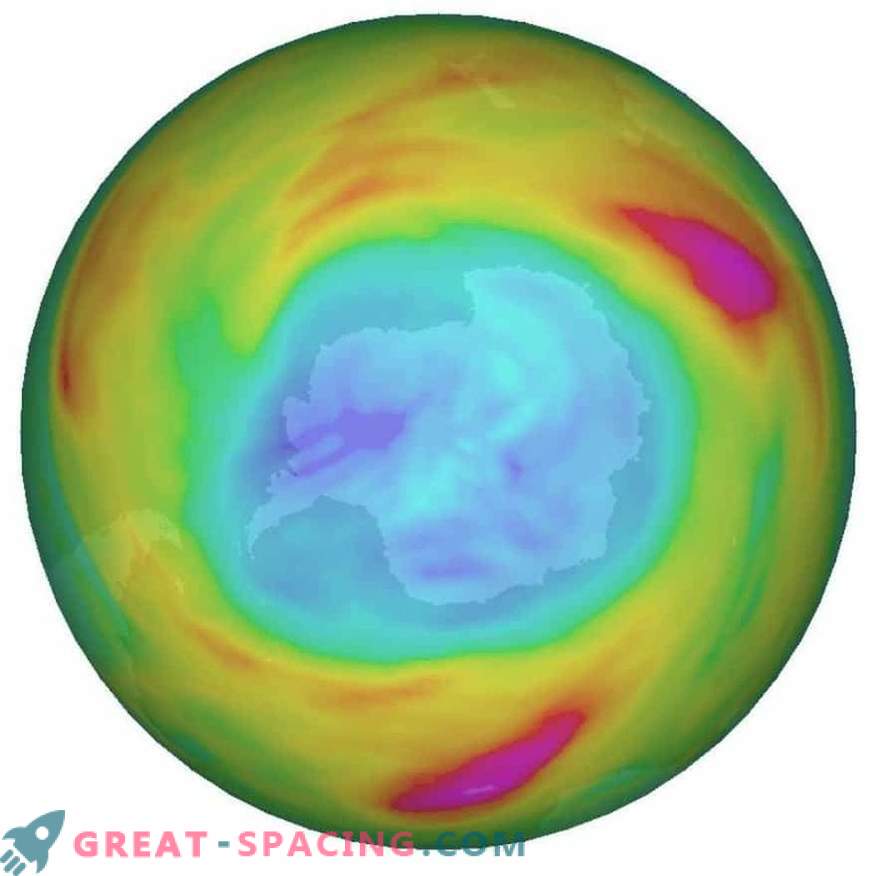
Ozone hole over Antarctica (September 4, 2018). Strong winds, referred to as the stratospheric polar swirl around the South Pole, play a significant role in the ozone depletion process at this time of year. Low ozone is marked blue, and high ozone is pink
The first results affect employees who have spent years creating and developing a mission. The Aladin device is especially pleased with its sensitivity. When activated, it turned out to gradually increase energy levels, checking it after each movement.

Aeolus mission will not only provide important information for improving weather forecasts, but also contribute to long-term climate research
Scientists believe that it was thorough preparation and testing that made the mission so remarkable in terms of functionality.