The unusual infrared radiation seen by the Hubble Space Telescope near the nearest neutron star may indicate that the pulsar is endowed with previously unseen features. A new study can help better understand the evolutionary path of neutron stars - the incredibly dense remnants of massive stars after a supernova event.
A specific neutron star belongs to the group of the nearest X-ray pulsars called the “Magnificent Seven” - they seem more red-hot than they should (taking into account their age and the available energy reservoir). The researchers monitored the broaching region in the infrared rays around the neutron star RX J0806.4-4123, whose total size covers 200 a. e. (2.5 times the Pluto orbit).
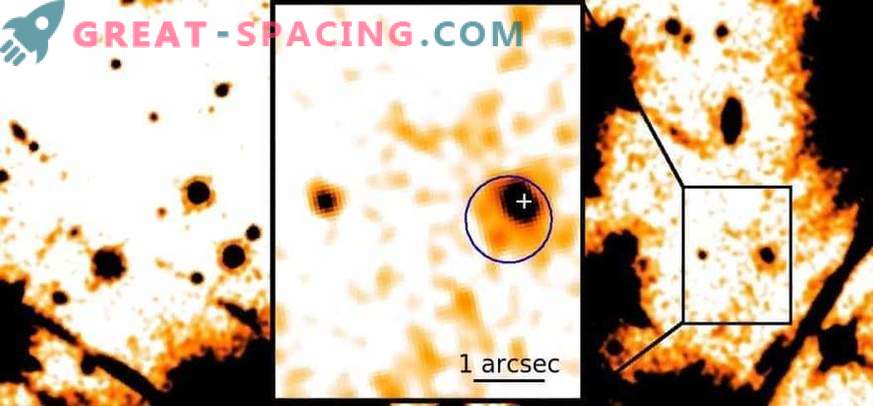
IR image of a neutron star with enhanced IR radiation, obtained in the Hubble Space Telescope survey. The blue circle is the position of the X-ray radiation of the pulsar (from Chandr), the cross is the location of the pulsar in the UV optics (Hubble)
This is the first neutron star, where the extended radiation is observed only in the infrared range. There are two possible explanations. Firstly, there is a disk of material consisting mainly of dust surrounding the pulsar. It will be represented by matter from a massive precursor star, and subsequent contact with a neutron star could heat the pulsar and slow its rotation. If so, then we will have to change our understanding of the evolution of the neutron star. Secondly, there is a wind pulsar nebula. The pulsary wind is formed when the particles are accelerated in an electric field created by the rapid rotation of a neutron star with a powerful magnetic field. The neutron star passes through the interstellar medium at a speed higher than the speed of sound, because of which a shock can form where the interstellar medium and the pulsar wind are in contact. Then the shock particles will release the synchronous rays, causing the observed enhanced IR radiation.
Neutron stars are usually studied in radio and high-energy rays, like X-rays. A specific study shows that new and unusual information about such objects can be obtained in the IR range. Researchers are awaiting the launch of NASA's James Webb space telescope in 2021 to continue exploring this space.