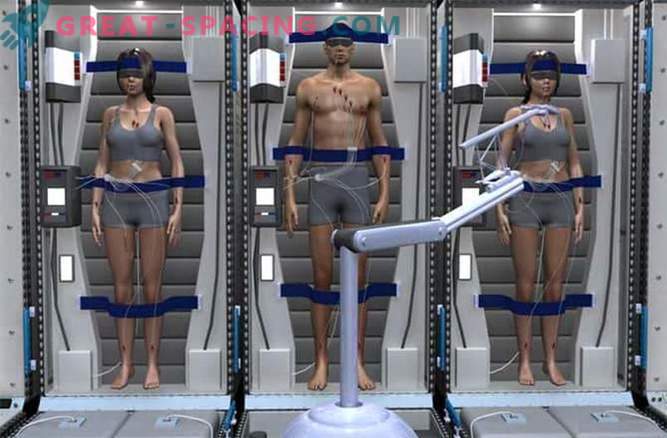
NASA is exploring an innovative way to drastically reduce the cost of a human expedition to Mars - to put the crew into a lethargic state.
Deep sleep, called lethargic, leads to a reduction in the metabolic functions of astronauts. This can be achieved through appropriate medical procedures. Lethargic sleep may also occur naturally in cases of hypothermia.
“Therapeutic lethargic sleep has been widely used from 1980 to 2003 in cases of critical trauma care in hospitals,” said aerospace engineer Mark Schaffer, from SpaceWorks, Atlanta. "This procedure is widely used in most major medical centers to induce therapeutic hypothermia on patients, which allows them to remain alive until they can receive the type of treatment they need."

In combination with intravenous nutrition, the crew can be placed in hibernation while traveling to Mars, which at best will take 180 days one way. Currently, the patient's life in a state of lethargic sleep is limited to about one week.
"We had to keep someone in this condition for more than seven days," continues Schaffer. "For a manned flight to Mars, we need to strive to increase this period to 90 or even 180 days."
From an economic point of view, the win looks impressive. The crew can be on the ship with fewer amenities, such as equipment, food, clothing and water. One of the projects is a rotating vessel, which will compensate for the loss of muscle mass and bone deformation.
The SpaceWorks study, funded by NASA, will reduce the amount of living space and the amount of consumables by a factor of three to five.
In general, this program will reduce the mass of the payload from 400 tons to about 220 tons.
"This is more than the payload of a large launch vehicle," said Schaffer.