The stars of the Milky Way appear in various parts of the galaxy, demonstrating certain trends in location and movement. However, there are especially capricious stars who do not want to fit into existing models.
Hyper Speed Stars
These are very unusual objects. In usual situations, stars move relative to each other at speeds of 10–20 km / s. A similar trend holds true for all residents of the drive. But let's move closer to the center and notice the changes. Local stars move at speed indicators of more than 200 km / s.
But this is not the limit! There is an unusual class of hyper speed stars capable of accelerating to 500-800 km / s! They are so fast that they literally burst from the clutches of their native territory and move closer to their sleeves, or even completely leave the borders of their native Milky Way, moving to a new galaxy.
Why is this happening?

Earlier it was thought that the whole thing was in the central supermassive black hole. Back in the 2000s. Scientists numbered 20 rogue stars who broke out of the Milky Way. They all moved from the center of the galaxy. Most likely, the speed is gained due to the gravitational contact with a supermassive black hole. There is also an option that they existed in pairs and began to accelerate due to the explosion of the second star as a supernova. With the scheme of the movement of the star from the center and “on the way out”, these scenarios seem quite convincing. Recently, however, powerful telescopes capture defectors who do not move from the galactic center at all. The latest outcast was the star LAMOST-HVS1.
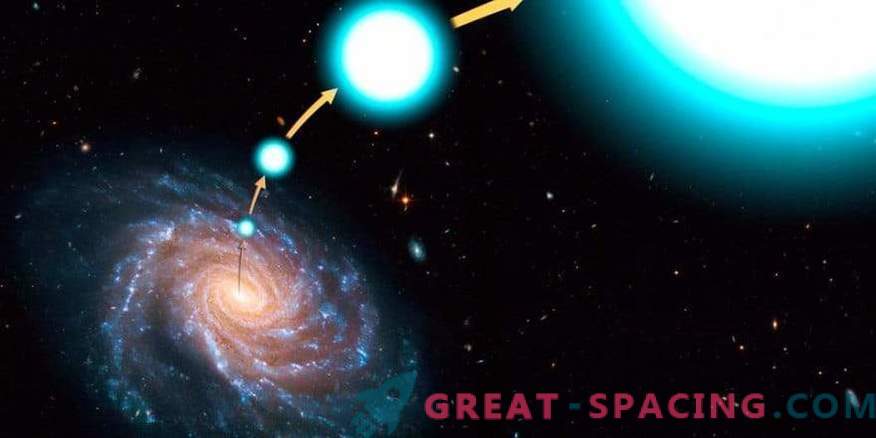
Stubborn Star Defector

LAMOST-HVS1 through the eyes of an artist
This blue giant 4 years ago recorded in the constellation of Cancer. The latest data was collected using the Gaia Space Telescope, which tracks stellar motion in the Milky Way.
But this star has become a remarkable outcast, because it seems the largest among those found. The hyperspeed giant is 9 times the solar mass. The star managed to escape far, so her homeland was not immediately found. But the reality turned out to be too strange. It turns out that LAMOST-HVS1 did not come from the galactic center, but from a small spiral arm.
With a speed of movement of almost 570 km / s, we can say that the escape began about 33 million years ago. It is most puzzling that there is not a single exact theory capable of explaining the situation of a specific object (there are no large-scale star clusters in the sleeve, and the star’s massiveness is too huge).
Postscript
One theory does exist, but it is difficult to prove. Perhaps, the acceleration from the sleeve could occur if the intermediate mass black hole served as a catalyst. But the existence of these objects has not yet been proved. Therefore, scientists are closely watching the star, which not only seems special in itself, but can also serve as a thread to detect the first black hole of intermediate mass.