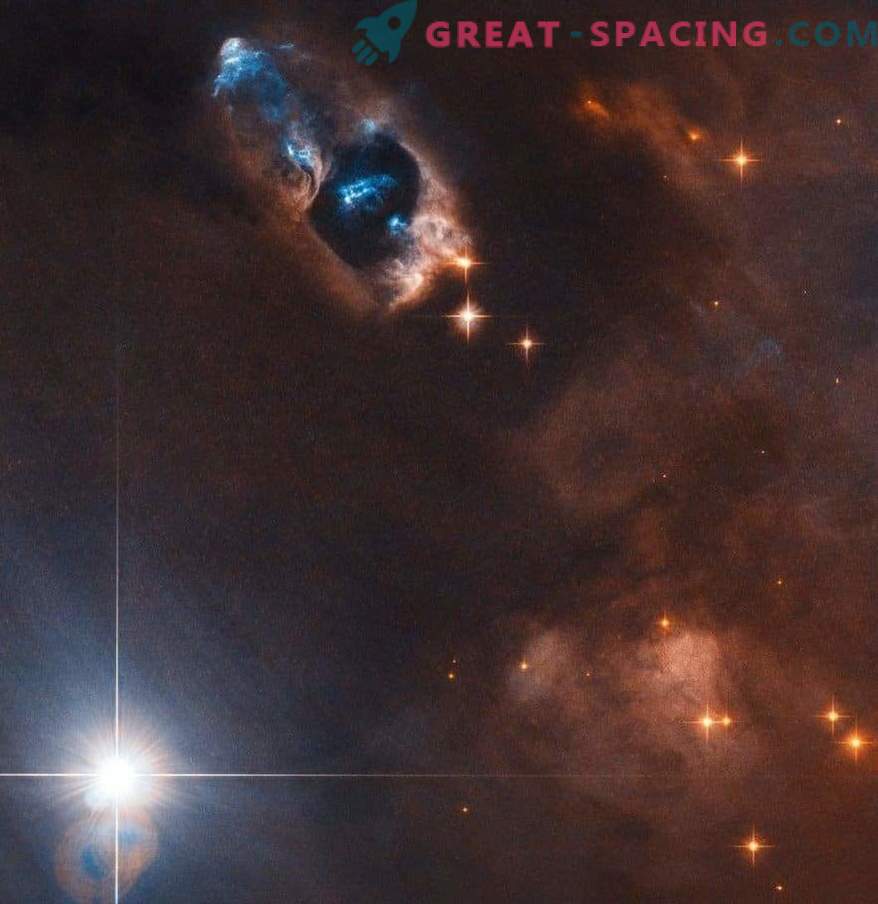
The photograph of the Hubble Space Telescope (NASA and ESA) was able to capture the “shot” of a newborn star, namely Herbig Aro objects from 7 to 11 (HH 7-11). These five objects, marked in blue in the upper central part of the frame, are located inside the reflective nebula NGC 1333. It is filled with gas and dust and lives at a distance of about 1000 light years from Earth.
Herbig-Haro objects, such as HH 7-11, are considered transient phenomena. Moving away from the star that created them at speeds up to 250,000 km / h, they disappear into oblivion for several tens of thousands of years. The young star and the source for HH 7-11 is called SVS 13. All five objects move from it to the upper left corner. The present distance between the star and the objects is 20,000 times greater than the Earth-Sun distance. Herbig-Aro objects appear when jets of ionized gas ejected by a young star collide at high speeds with the nearest clouds of gas and dust. Objects captured in the frame are not exceptions and appeared when the streams of the newborn star SVS 13 crashed into the surrounding clouds. These collisions created five bright bunches of light inside the reflecting nebula.