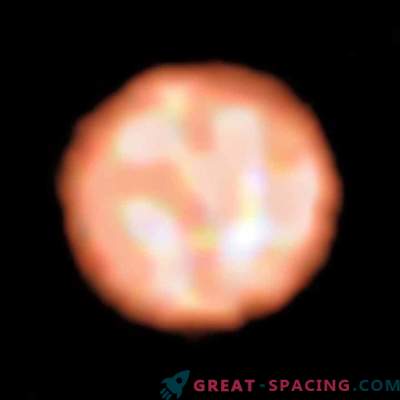
A blue hyper-giant resides at a distance of 65 million light years, which once existed inside the group of young stars of the spiral galaxy NGC 3938. In 2017, the star exploded as a supernova. Archive photos of the Hubble Space Telescope were used to detect the doomed predecessor star, as it looked in 2007.
The star could massively reach 50 solar and burn at an incredibly fast speed, red hot and becoming bright blue. The object was so hot that it lost the outer layers of hydrogen and helium. During the explosion, astronomers classified the star as an Ic-type supernova due to the absence of hydrogen and helium in the spectrum.