Silicon dioxide makes up about 60% of the earth's crust and one particular form (quartz) is the main ingredient in sand.
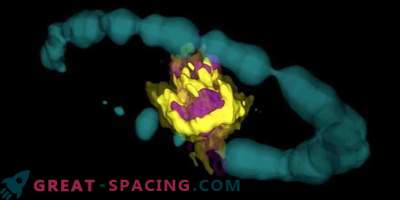
The next time you look out the window for inspiration, keep in mind that concrete material is forged into the heart of an exploding ancient star. An international team of scientists reported that they found silicon dioxide (the main component of glass) in the remains of two supernovae, billions of light-years distant from Earth.
The researchers used the NASA Spitzer space telescope to analyze the light emitted by a decaying mega-cluster and obtained the signature of silicon dioxide based on a certain wavelength of light.
A supernova appears when a big star spends its own fuel, which leads to a catastrophic collapse. All this action ends with an explosion of galactic proportions. It is in these celestial catastrophes that individual atoms merge, forming many common elements, including sulfur and calcium. Silicon dioxide makes up about 60% of the earth's crust, and one of its forms (quartz) is considered the main component of sand. In addition, glass windows, fiberglass and industrial concrete are made from it. A new study showed for the first time that the amount of silicon dioxide created by a supernova is sufficient to make a significant contribution to dust throughout the universe. As a result, it could form and create the Earth.
Every time you walk on the sidewalk, look out the window or walk on the sandy beach, you come into contact with material created by exploding stars millions of years ago. In 2016, they reported that they found traces of lithium (used in the manufacture of modern electronics) at the base of a rotating new one.