A star lives in some five hundred light years from us, in the constellation Cygnus, which, although smaller and redder than the Sun, but also, like our star, may have a planet like a twin similar to our Earth.
Having a diameter of only 10% more than the Earth’s, the newly found world is the first closest in size that “heats up” near its star, being in a temperature-friendly temperature range at which water, if it exists there, can be in liquid the form.

Scientists, hunters for the twins of the Earth, focus on planets that may have on their surface in the form of lakes, oceans or puddles of liquid water necessary for the flow of the “chemistry” of life.

Comparative sizes of Kepler-186F and the Earth
Statistically, the number of planets similar to the Earth, rotating in admitting the possibility of life orbits (not too far so that the water does not freeze, not too close to the star, so that it does not evaporate), should be not small, show recent studies.
But to conduct such a search is extremely difficult, given such a long distance. NASA’s “Kepler” space telescope spent four long years observing approximately 150,000 selected stars and trying to detect small fluctuations in the intensity of their radiation, which could be caused by planets rotating around them, crossing the line of observation and dimming the star for a short time.
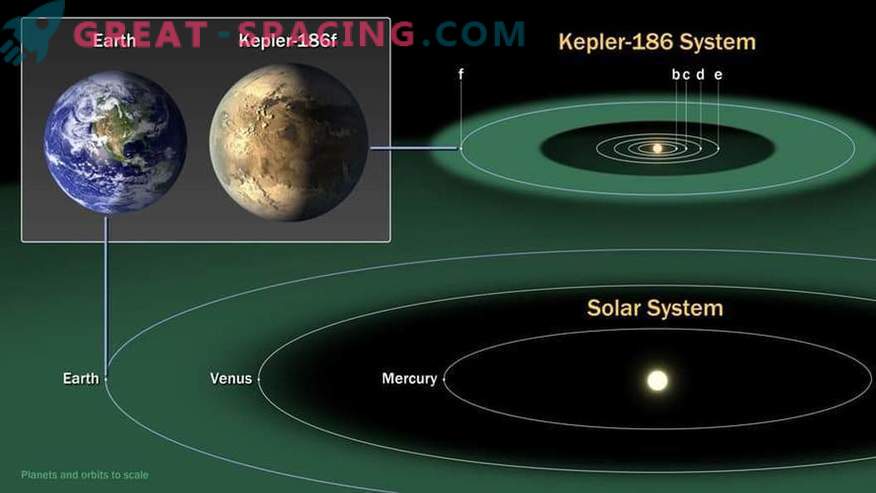
Comparison of Kepler-186F orbits and the Earth
“A planet the size of Earth, located from its star-mistress, similar to the Sun, as far as our planet from our luminary, should“ block ”only 80 - 100 photons of light from a star of every million. And it will only do this once every 365 days, ”said astronomer Thomas Barclay of the Kepler scientific group at the Moffett Field Research Institute (NASA, California).
The smaller the size of the star around which the twin of the Earth rotates, the easier it is to detect the movement. The newly discovered planet, called “Kepler-186F”, blocks about 400 photons of star light from every million when crossing the line of observation, and this is repeated every 130 days.
“I’m not claiming that this planet is habitable, but our discovery is an important milestone in the search for them,” Barclay said in an interview with Discovery News. “She is not a twin of Earth, but perhaps she is her cousin”