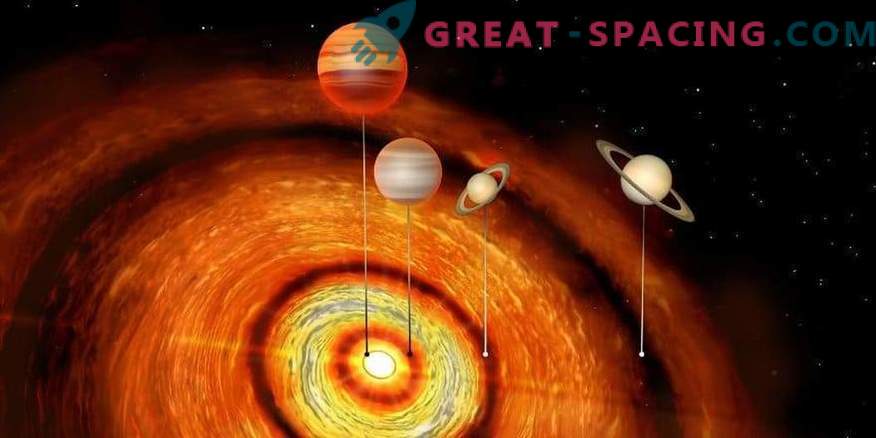
Scientists have found a young star with four giant planets like Saturn and Jupiter in orbit. This is the first time that such a large number of massive planets have been fixed near a young star. The system also broke the record for the most extreme range of orbits: the outermost planet is 1000 times farther from the star than the innermost one. All this raises many questions regarding the formation of the system.
The star is only 2 million years old, which in astronomical terms is considered a “child”. Around her there is a large-scale disk of dust and ice. This is a protoplanetary disk, including planets, moons, asteroids and other objects. The star is known for having a hot Jupiter - a massive planet resembling our giant. Although hot Jupiters are the first type of exoplanets to be detected, their presence has long puzzled astronomers. The fact is that they are too close to the parent stars.
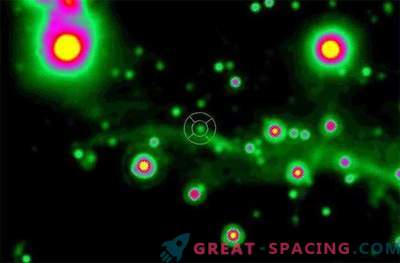
In a new study, scientists used the ALMA submillimeter array to search for other planets near this young star. The pictures managed to notice three different spaces on the disk, caused by three additional gas giants. The CI Taurus star is 500 light-years distant from us in a highly productive area of star birth. Its 4 planets are very different in orbits: the closest is in the place of our Mercury, and the furthest is 3 times farther from Neptune. The two outer planets resemble Saturn in mass, while the inner ones are 1 and 10 times the mass of Jupiter.
The discovery raises many questions. About 1% of the stars are sheltered by the hot Jupiters, but most of them are hundreds of times older than CI Taurus. It is difficult to say whether this is a common case or an exception. Scientists do not know whether the related planets played the role of bringing the planet closer to the innermost orbit and whether such a mechanism would work in other systems. It is also not clear how the two outer planets were formed.
It is difficult to work with models because they focus on known observations, and this is a new phenomenon. Planets like Saturn should form, accumulating first a solid core, and then attracting gas from above. However, these processes are extremely slow at large distances from the star. Scientists plan to explore the mysterious system in several wavelengths and get more data on the properties of the disk and planets.