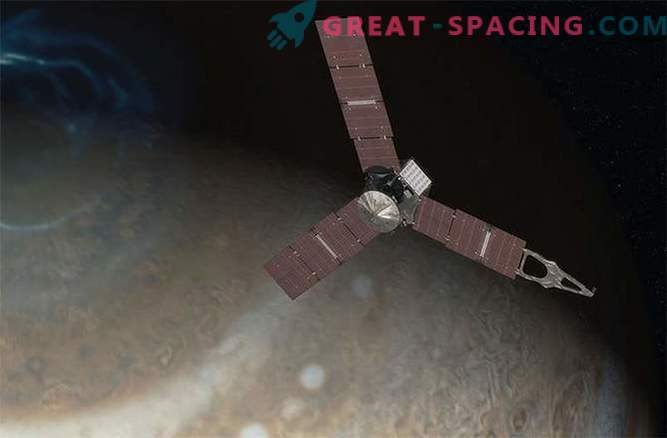
Juno - a mission that seeks to meet with Jupiter in July 2016.
In the announcement of this amazing mission to the largest planet of the solar system, some of the scientific and engineering problems of Juno are explored.
Water

We often talk about water on the icy moons in the outer solar system, such as Europe in Jupiter. But it is not known whether Jupiter itself has water. The upper atmosphere was actually watered with water from comet Shoemaker-Levi-9 in 1994. The water was discovered in 2013 by the Herschel Space Observatory, in areas close to those where comet fragments crashed into the atmosphere.
Water in other parts of the atmosphere may have emerged during the formation of Jupiter, when ice planetesimals were abundant in the solar system. Looking at the water and other elements on Jupiter, there is a feeling of how the Solar System looked, because Jupiter, unlike our planet, is very close to the original formations. (Earth received a new atmosphere through plants and volcanic eruptions, among other factors).
Aurora
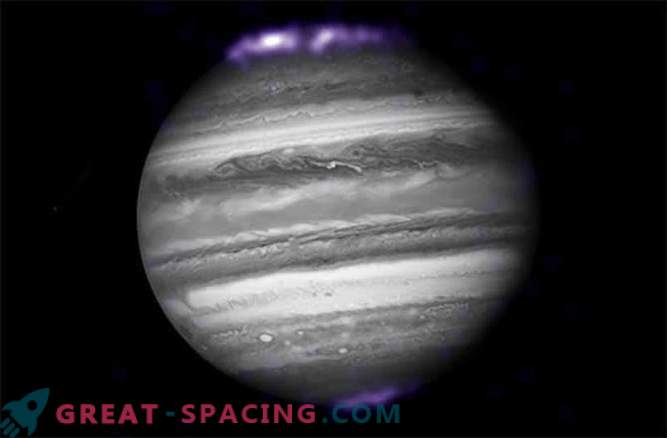

Jupiter has a huge and powerful magnetosphere, which is largely manifested in the strength of its auroras. The problem is that several long-term observations of distant planets are expected, where Juno will have an advantage over observatories, such as the Hubble Space Telescope, which can be monitored only occasionally. The key to the bright aurora of Jupiter is due to the compression of hydrogen in the intense gravity of the planet. It becomes metallic hydrogen, and this fluid is highly conductive. Juno will see charged particles and magnetic fields on Jupiter close up in order to make predictions for other major planets in our Solar System and in other places.
Gravity

The enormous gravity of Jupiter is a blessing when we try to send a spaceship far into the solar system. We used a giant planet to increase speed for such missions as Voyager and New Horizons. The bonus with these maneuvers is that researchers usually include cameras and some tools to add scientific knowledge about Jupiter.
The role of Juno is to study the field of gravity in detail to learn about any changes and the reasons for their occurrence. Fluctuations in gravity may indicate changes in the internal structure of the planet.
Atmosphere
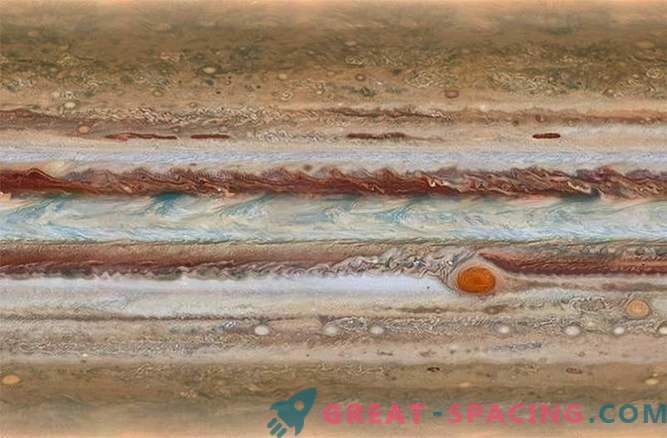

One of the atmospheric secrets of Jupiter - why the Great Red Spot is shrinking. This feature has been part of Jupiter for at least 400 years (since we have telescopes), but it is becoming less and less for reasons that are poorly understood. The shrinkage rate also varies from year to year.
The image of Hubble, which you see here, also shows a rare wave structure that was visible only once in 1977 in pictures taken by the Voyager-2 mission. For its part, Juno will display the depth of penetration of these colorful features into the atmosphere, as well as for the first time to track the movement of fluids below the clouds.
Engineering
While Juno is focused on science, the spacecraft itself will also be a useful research item for planning future long-term missions. Juno is actually the most far-flung spacecraft using solar energy, which he passed this milestone this month. This was made possible due to the increased energy efficiency of instruments and spacecraft, as well as higher performance of solar cells.
As in all missions, scientists will investigate how well a spacecraft has been working for a long time. When something breaks (which is inevitable), the team will try to find a way to fix it. They will also strive to develop a new generation of this technology to avoid damage on the following spacecraft.