In the 1990s it was possible not only to predict the fall of a comet on a large planet, but also to fix this event with the help of a spacecraft. It is about the collision of the comet Shoemakers-Levy 9 with Jupiter.
Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9
The comet was discovered only in 1993. The find belonged to spouses Schumaker and David Levy. The analysis showed that the year before the object approached a dangerous distance to the upper cloud layer of the gas giant, because of which the crushing process occurred. Therefore, astronomers have discovered not a comet, but rather a cluster of 21 two-meter fragments flying in space.
Unlike many comets, the Shoemaker-Levy 9 object orbited the planet, and did not arrive suddenly. This allowed the researchers to conduct detailed observations and determine the time of the fall.

Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9, named after the discoverers, was often referred to as the comet “pearl string”. Known for an impressive view, as well as a collision with Jupiter! The primary single nucleus of the comet was torn apart by the strong gravitation of the gas giant during its close span in 1992. The fragments (on the right) are visible in a photograph of the Hubble Space Telescope (resemble pearls on a thread). In July 1994, these comet pieces collided with Jupiter. The fragments fell to the surface of Jupiter on July 16-22, 1994 at a speeding acceleration of 64 km / s, which led to the formation of large fluctuations in the clouds of the gas giant. The event was observed by many scientists from Earth, but the visibility was poor, because everything happened on the opposite side of our planet.
Overview from the spacecraft
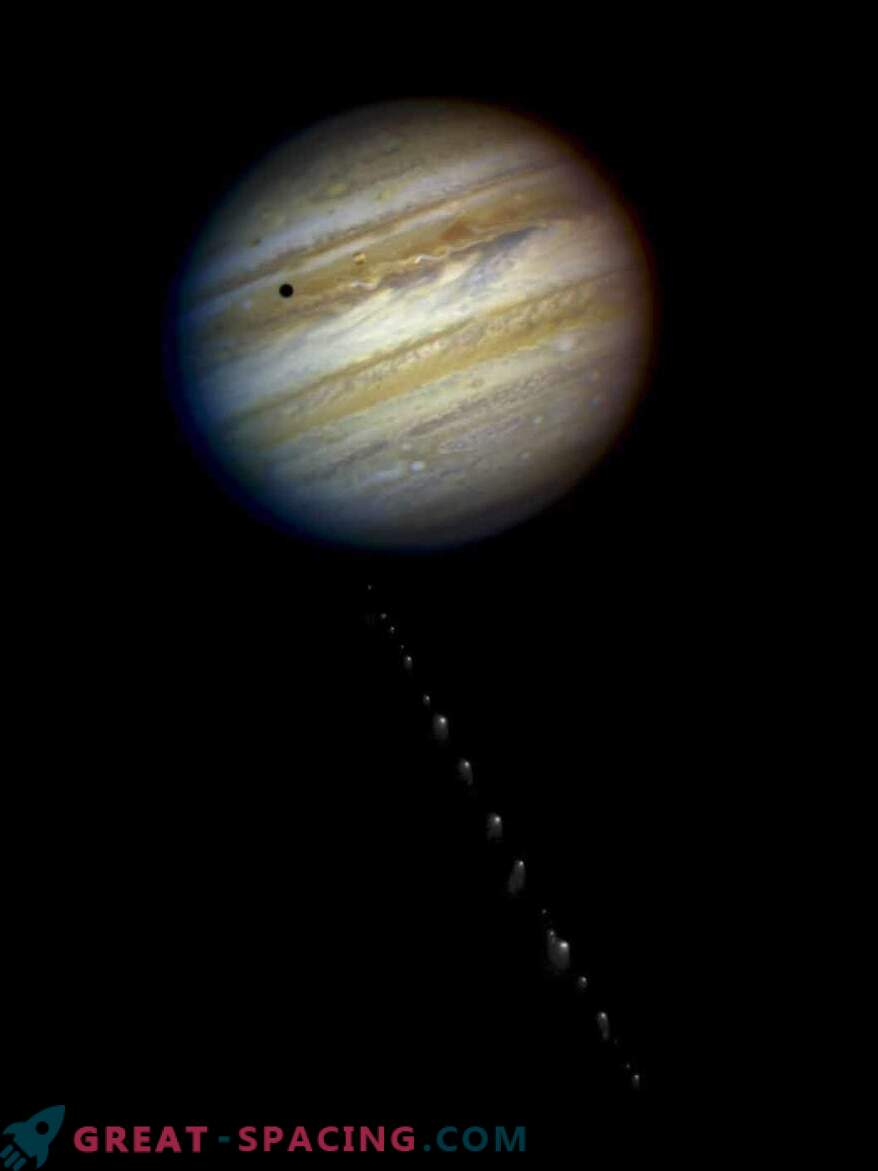

This image was compiled from individual images of Jupiter and Comet Shoemakers-Levy 9 taken with the Hubble Space Telescope in 1994.
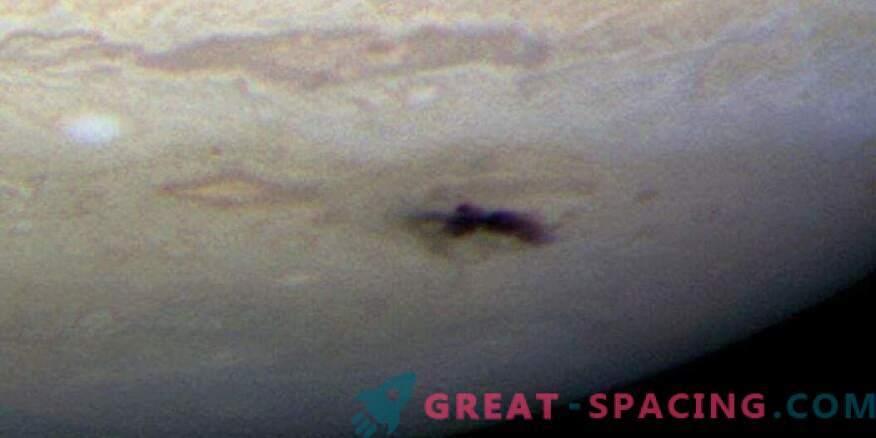
However, flares and scars were able to be examined close by thanks to the Galileo spacecraft. At that time it was located at a distance of 1.6 a. e. from the gas giant. In the places of falling on the surface “scars” were formed in the form of dark areas, which lasted for several months. If we take the total coverage from all the fragments, then the sizeable storm exceeded the Big Red Spot.
Interestingly, the fall of the comet also caused bright lights at the poles of the gas giant. Each event of the collision was accompanied by a powerful explosion and a bright flash. It is believed that a collision even with one such fragment for our planet could end in disaster.
Postscript
Jupiter is sometimes called the terrestrial defender, because in ancient times it could obscure us from the arrival of comets and large asteroids, having taken a blow upon itself. In favor of this theory, the event of 2009 is triggered, when another space object crashed into Jupiter.
Scientists have recorded not the moment of the fall, but the dark spot that has formed. The analysis showed that the original object (possibly an asteroid) covered in the size of 200-500 m, emitting, when it fell, an energy comparable to 5 billion tons in trotyl equivalent.