A team of Hungarian astronomers and physicists may have managed to confirm two elusive clouds of dust in semistable points at a distance of 400,000 km from Earth. The clouds were named after the Polish astronomer Kazimierzhem Kordylevsky, who reported them in 1961. However, they are too weak, so for a long time they could not confirm.
The Earth-Moon system has five points of stability, where gravitational forces maintain the relative position of objects located there. Two of them are called Lagrange points L4 and L5, which form an equilateral triangle with the Earth and the Moon, moving around the planet as the Moon moves in its own orbit.
L4 and L5 cannot be called 100% stable because they are influenced by the gravitational attraction of the Sun. However, these are places where interplanetary dust is capable of collecting, at least temporarily. Kordylevsky observed two adjacent clusters of dust in L5 in 1961. But scientists doubted existence due to the weakness of the clouds.
In early 2018, the Hungarian scientific team modeled the clouds of Kordylevsky to evaluate the process of their formation and how they can be detected. The researchers were interested in their detection using polarizing filters that transmit light with a specific direction of oscillation.

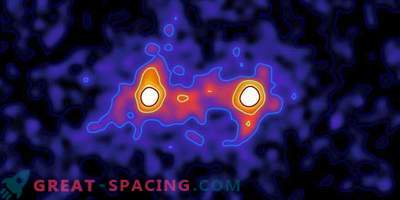
The structure of the angle of polarization of the sky around the Lagrange point L5 of the Earth-Moon system, measured by photo polarimetry in the green (550 nm) spectral range on August 19, 2017. Position L5 is marked with a white dot. The central region of the dust cloud (bright red pixels) is also visible in the picture. After that, scientists began to search for dust clouds. With the help of a linear-polarization system of filters, they mined the exposure of the proposed location of the Kordylevsky cloud at point L5.
The resulting photos show polarized light reflected from dust that extends beyond the field of view of the camera lens. The observed picture corresponds to the early predictions made 60 years ago. The group was able to eliminate optical artifacts and other effects, which speaks in favor of the existence of clouds of dust.
Due to the relative stability, L4 and L5 points are considered as potential locations for orbital space probes as station locations for more in-depth observation of the Solar System. Researchers will study this area and the clouds to see how stable they are and if there is the slightest threat to equipment and astronauts.
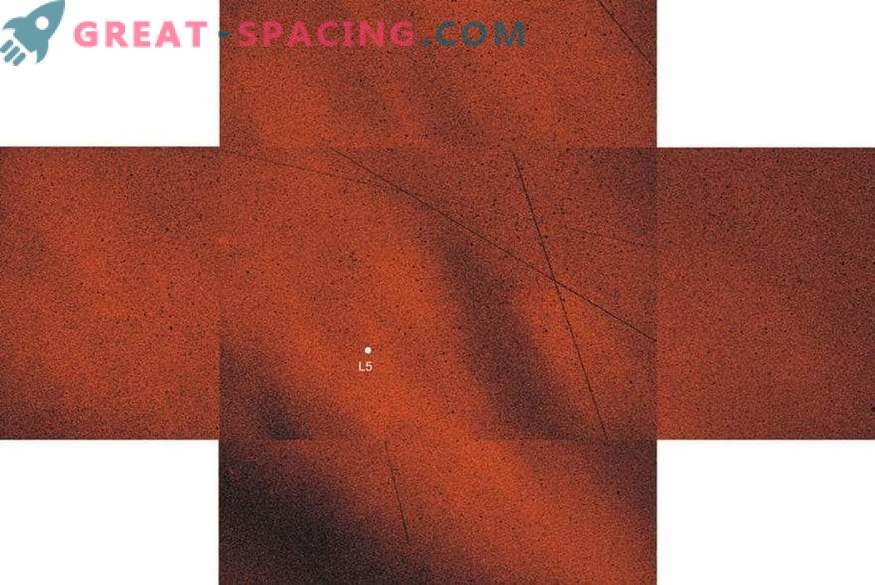

Mosaic of the angle of polarization around the angle of the point L5 (white point) of the Earth-Moon system. Five rectangular windows correspond to the fields of view of the polarimetric telescope