Where is the line beyond which the new world begins and ends the usual Solar system? Usually we are limited to only the Earth and the nearest planets. But let's walk along the native system, move away from the star as far as possible and see where the edge is located.
Planets of the Solar System

Computer illustration of NASA shows the planets of our system. Scale does not transmit true orbits
Borders in the usual sense are determined by the sphere of influence. In our case, we are talking about the gravity of the star, which all other celestial bodies obey, revolving around the sun. Thus, in the Solar System, it is possible to visually make several sectors, where the gravity decreases with increasing distance from the star.
Many do not look beyond the planets of the system, believing that this is the end of it. Officially, 8 worlds rotate around a star (Pluto became a dwarf planet in 2006), so Neptune closes the chain.
This sector is divided into internal and external systems. The first category includes the four terrestrial planets closest to the Sun, also the main asteroid belt and closes the dwarf planet Ceres.
In the outer group there are giant planets (gas and ice), including the hypothetical Ninth Planet (Planet X), comets and centaurs. Neptune is an average of 4.55 billion km away from the Sun.
Moving to the Kuiper Belt
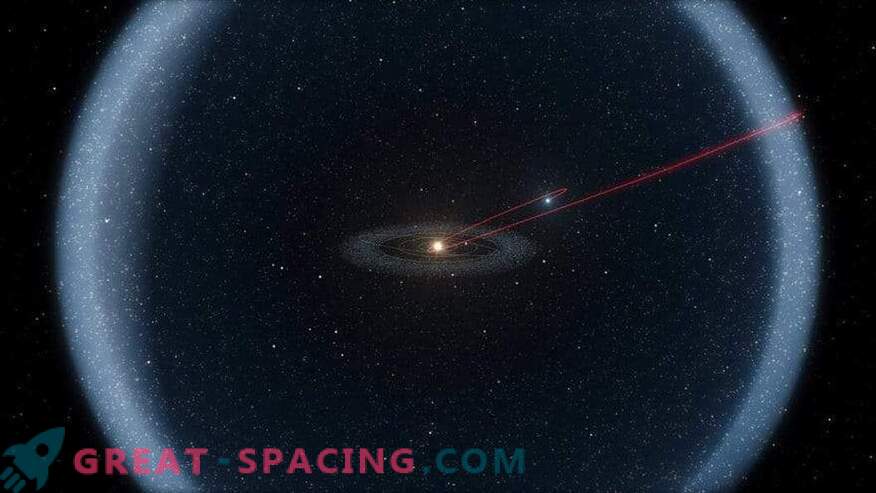

Comparing the scale of the inner solar system, Kuiper Belt and Oort cloud We fly past Neptune, and it turns out in a circle of trans-Neptune objects. There is little information about this site, but it is believed that it is filled with small celestial bodies, represented by ice and stones.
Further, at a distance of 30 a. e. from the Sun begins the Kuiper belt, extending to 55 a. e. In fact, this is a kind of asteroid belt, which we met between the outer and inner solar systems, but it is 20 times wider and can be 200 times more massive.
In the Kuiper belt there are small objects from the ice, as well as at least four dwarf planets, among which are Pluto, Haumea, Makemake and Eris. There is also a scattered disk. It is believed that from this territory comes a greater number of short-period comets, whose orbital period is less than 200 years.
We leave to heliopause
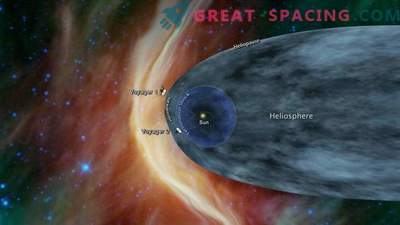
After the Kuiper belt, everything becomes foggy, because it is difficult to understand exactly when the interstellar space begins. We are slowly moving to the area of the solar space - heliosphere. Here the plasma of the solar wind moves in relation to our star at supersonic speeds.
At a distance of 85-95 a. e. from the star, the solar wind begins to slow down and a feature of the shock wave appears. It is this threshold that the spacecraft Voyager-1 and Voyager-2 passed through in 2004 and 2007.
Overcome another 40 a. e. and note the collision of the solar wind and interstellar matter. Friends, we ended up in the heliopause, which in form resembles a bubble slightly stretched from the Sun. These distances seem incredible, but in 2018, Voyager-2 managed to overcome the heliopase and get into interstellar space, and the Voyager-1 probe did this in 2012.
Mysterious Oort Cloud
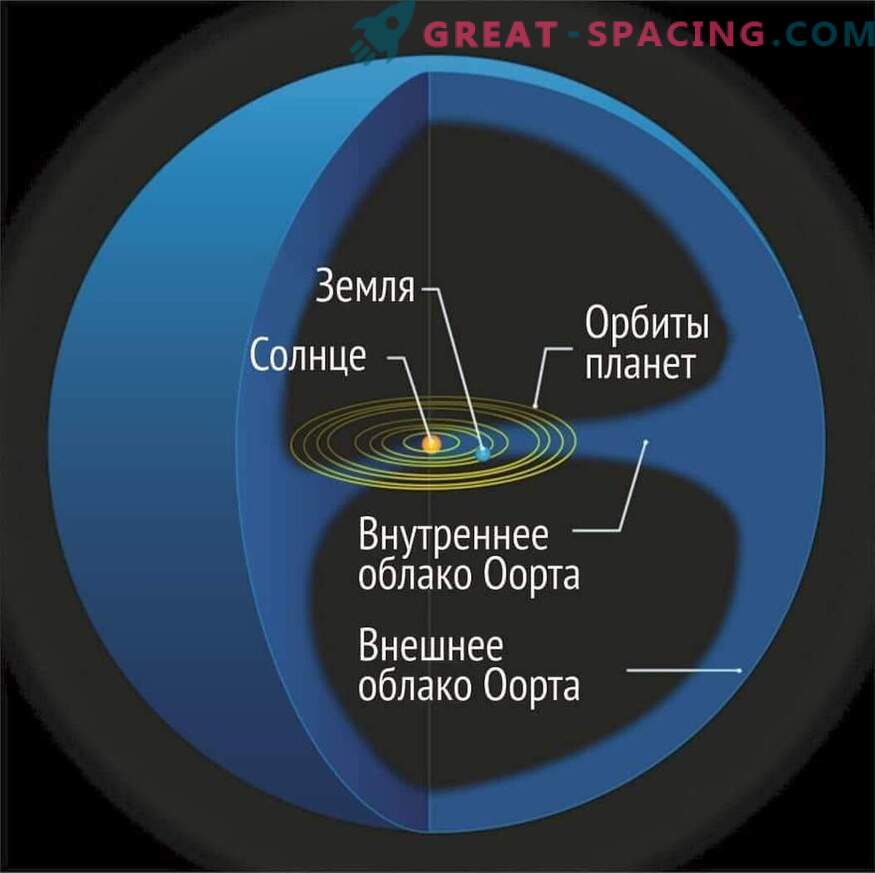
Oort cloud structure
This is still a hypothetical territory capable of being a haven for long-period comets. It is believed that it begins at a distance of 50,000 a. e. from the Sun and extends to 100,000 a. e. This is a spherical cloud capable of accommodating a trillion icy celestial bodies. Some believe that large planets and even Planet X may be hiding here, but the probability is extremely low.
Last Bounds
Not a single spacecraft has managed to overcome interstellar space, the Oort cloud, and escape further. Therefore, scientists can only guess. There is a theory about the existence of boundary line, where the star satellite of the Sun Nemesis resides, but there is no evidence yet. While it is believed that solar gravity extends to 125,000 a. e. and this can be considered the limits of the solar system.
Postscript
Voyager will reach the Oort cloud no earlier than 300 years from now, so our generation was not destined to celebrate this amazing event. These scales are shocking, but this is just the limits of our system. Recall the whole Milky Way galaxy, which is in a cluster, a group, followed by even larger structures.