It seems that everything is simple: by definition, comets are objects that leave a long tail behind them as they approach the Sun, while asteroids are deprived of this. But it turns out that this is not always the case. Since 1996, we know that some asteroids have long tails of dust, similar to those of comets.
“Object 133P / Elst-Pizarro is the prototype of“ active asteroids, ”says Jessica Agarwal, a scientist at the Max Planck Institute for Solar System research.
From the moment of their formation, comets remained in the outer part of the Solar System and begin to fall into its inner part only recently. This means that most of the original ice has been saved. However, a typical asteroid remains in the Asteroid Belt, located between Mars and Jupiter, heating up on the Sun for billions of years. Therefore, scientists are trying to understand how asteroids can remain active when most of their ice is likely already melted.
Agarwal tells us about the processes by which an asteroid can behave like a comet, as well as the latest observations of its team on the 288P / 300163 object using the Hubble Space Telescope.
Collisions
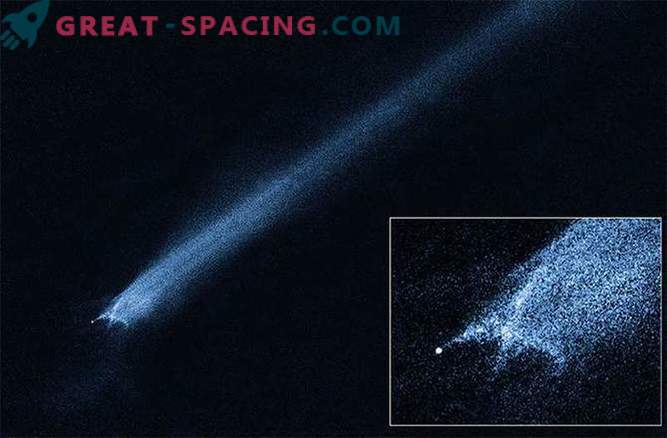

Even a random Star Wars fan can have a distorted view of what an “Asteroid Belt” is and how it looks. In the “Empire Strikes Back” part, the Millennium Falcon constantly evades cosmic rocks. In fact, the asteroids between Mars and Jupiter are located hundreds of thousands of miles apart. This is a rare event when they collide with each other. “As a result of such a collision, a simple crater may form or catastrophic destruction may occur. It all depends on the size, speed and internal forces,” Agarwal said in an e-mail "In any case, the collision will generate a dust cloud, and this is the cloud that we see from Earth, and makes the asteroid look like a comet."
“One such example was 596 Scheila, which hit a much smaller asteroid in 2010 and produced two temporary clouds of dust. The scar on the surface became noticeable due to a change in the light curve of the object,” Agarwal added.
Rotation

“If an asteroid rotates fast enough, sometimes dust and other particles will fly away from its surface. The fastest asteroids can even break themselves. Everything will again depend on their internal forces. But how an asteroid can change its rotation speed “One option is if the asteroid has an irregular shape or an uneven reflective surface (or albedo), emitting uneven thermal radiation. Such an effect is known as the“ YORP effect ”."
"In some cases, this effect can spin the asteroid to the limit," said Agarwal. "A striking example of catastrophic decay is P / 2013 R3, which broke up at least 10 fragments at the end of 2013, as well as P / 2012 F5, which has a critical rotation period and throws fragments and dust."
Ice Loss

“We have already indicated earlier that asteroids are in constant interaction with solar radiation. So what ice can remain in billions of years? Scientists assume that there should be some more ice inside the object, which due to external influence can erupt outward”, - said Agarwal.
"Such activity usually lasts for several weeks or months while solar radiation is strong enough. Currently, such activity is seen on four asteroids. One of these is the prototype 133P / Elst-Pizarro."
Cracks when heated

“If the material heats up quickly, thermal expansion cannot be uniform. The surface tends to suffer most from solar heating than the inner layers. In addition, different materials react differently to heat,” Agarwal writes. "As a result, a rapid change in temperature can cause the surface to crack, from which dust can be spewed."
One such example is the asteroid 3200 Phaethon. Scientists believe that it will come too close to the Sun and will heat up to 700 degrees Celsius. Given its fast rotational speed and heat load, catastrophic changes may occur. Astronomers are already observing bursts of dust from the asteroid.
Hubble Study

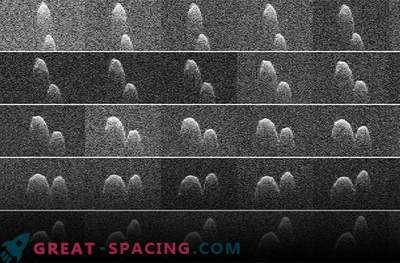
A huge advantage of the Hubble Space Telescope is its location above the earth's atmosphere. This allowed him to detect the dust tail of an active asteroid 288P / 300163, which is only 1000 km (621 miles) thick and extends 50,000 km (31000 miles) from the heart of a comet or nucleus. This thin trail speaks of the release of dust from the surface of the asteroid.
The researchers suggest that ice melts on the surface of the 288P, while freeing dust.
"As a supplement, we found that the state of the nucleus changed between our two observations, divided by about a week," she said. "One possible explanation could be that the 288P has a binary core, but we really need more data to confirm this."