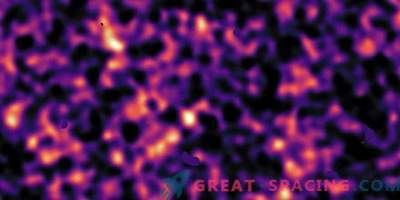
In 2014, with the help of the Hubble telescope, it was possible to fix a giant galactic cluster, which is 3 million billion times greater than the solar mass. Therefore, under the official name ACT-CLJ0102-4915 he was nicknamed “El Gordo” (from Spanish - “fat”). This is the largest red-hot galactic cluster.
Such structures are considered the largest objects in space, whose connection is supported by gravity. The formation takes billions of years, where small galactic groups gradually merge into a large structure. The 2012 survey from Chandra, the Very Large Telescope and Atacama showed that we have two galactic clusters colliding at a speed of a million kilometers per hour. The formation of galactic clusters strongly depends on dark matter and dark energy, so the study of these structures will allow a better understanding of the nature of unknown substances. In 2014, it was discovered that most of the El Gordo mass is hidden in the form of dark matter. Normal matter is represented by a hot gas glowing in X-rays. In a collision, the gas slows down, but dark matter does not.
An improved camera and a wide-angle camera 3 were used for the image. The survey was carried out as part of the RELICS program, which displayed 41 massive galactic clusters in order to search for the most distant galaxies (they will be observed by the telescope James Webb).