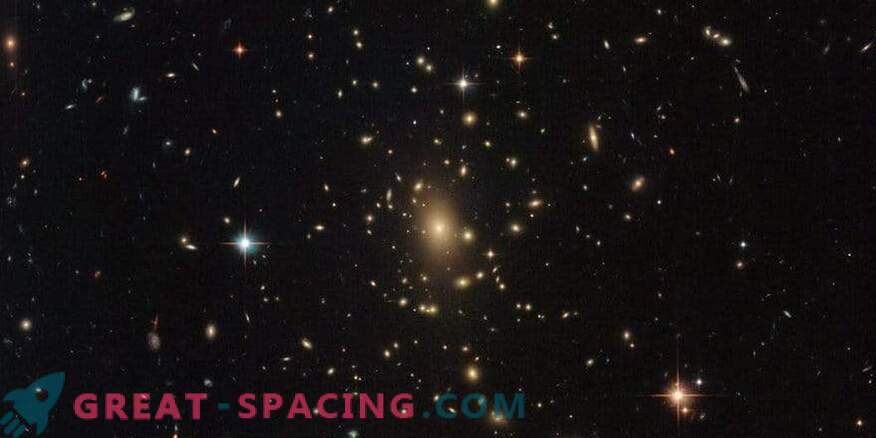
This is a real treasure chest. In the foreground are the bright stars of the Milky Way. Then the curls of several spiral galaxies flash, and the central set of bright objects is a massive galactic cluster. Such clusters are considered to be the largest objects in space, held together by gravity. Capable of containing thousands of galaxies of various shapes and sizes. Usually their mass is a million billion times the size of the sun!
This massiveness makes clusters useful as they become natural tools for testing astronomical theories, like Einstein's general theory of relativity. It says that objects with a mass distort the fabric of space-time around them. The greater the mass, the greater the distortion. As a result, the giant cluster has a serious impact on spacetime, distorting the light from more distant galaxies and enhancing the radiance. This phenomenon is called gravitational lensing. The picture was taken using the Hubble advanced camera and wide-angle camera 3 as part of the RELICS program. The project managed to display 41 massive galactic clusters in order to search for the most distant galaxies. They will become targets for the future of the James Webb space telescope.