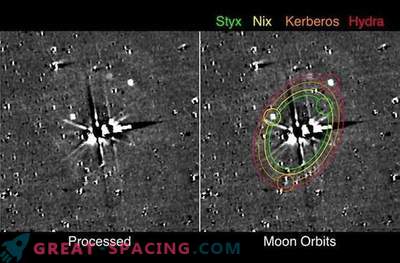
For many decades, the environment of Pluto with its satellites looked like a collection of bright spots even from powerful telescopes. Today, a dwarf planet with its family of five satellites was photographed in great detail due to the flight of the New Horizons spacecraft.
During the span week, a “family portrait” of the Pluto system was made, among which was the satellite Kerber, which was not known until 2011.
This image was taken from four separate images that were captured with the LORRI camera (short for Long Range Reconnaissance Imager) of the New Horizons mission. The image was taken in a few hours of the flight of the spacecraft on July 14, 2015, when New Horizons flew over Pluto at a distance of 7800 miles (12,500 km), which is smaller than the diameter of the Earth.
Named after the three-headed dog, which protected the gates to the underworld in ancient Greek mythology, the satellite Kerber has not three heads, but rather two blades, unlike comet 67P / Churyumov-Gerasimenko. It is believed that the satellite Kerber as 67P formed due to the connection of two smaller objects. Kerber has a width of about 7, 4 miles (12 km) and is covered with water ice.
Based on the first observations from the Hubble Space Telescope, scientists assumed that Kerber is more massive than other small satellites Pluto. The data obtained with the help of New Horizons showed that it is not.
“Our predictions about Kerber did not come true,” said researcher M. Showalter of the SETI Institute.
High quality images continue to flow to Earth, although New Horizons are moving further and further away from the dwarf planet. Having obtained and analyzed them, scientists will be able to establish complex interactions between Pluto and its satellites.