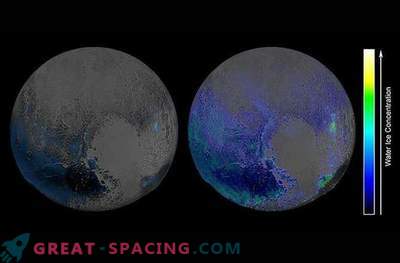News about floating ice and a surprisingly long haze - these are the latest discoveries provided by the NASA New Horizons mission. They argue that distant Pluto is an incredible icy wonderland.
“We suspected that flying to Pluto would give real surprises. It took 10 days after the closest approach, and we confidently say that reality exceeded all our expectations, ”said NASA Administrative Assistant John Gransfeld. “From the ices discovered, the exotic chemical surface, the mountain ranges and the vast haze, one can judge of the rich geology of the planet, which is certainly amazing.”
It took only seven hours after the approach to the maximum distance and the New Horizons sent their camera LORRI to reconnoitre. They managed to catch a glimpse of the light that had broken through the atmosphere, and saw that there was a smoke at an altitude of 130 kilometers. According to preliminary researchers, it became clear that there are two different layers: the first is located at around 80 kilometers, and the second is at a height of 50 kilometers.
“I stood for a long time with my mouth open when I received the first picture of the atmosphere in the Kuiper belt,” says the main investigator of the mission New Horizons at the Southwestern Research Institute in Boulder, Colorado Alan Stern. “It reminds us that intelligence gives us more than just unexpected discoveries; it gives extraordinary beauty.” The study of the structure of the atmosphere gives a chance to understand what is happening on the planet itself.
“In the haze that we saw in the picture, there are major points for creating complex hydrocarbon compounds, because of which the planet teaches a specific red tint,” said George Mason University researcher in Fajfax, Virginia Michael Summers.
Experts came up with models that show how to create haze. The fact is that ultraviolet sunlight is divided into gas and methane particles. Due to the decomposition of methane, complex hydrocarbon gases: ethylene and acetylene accumulate. They were also seen in the atmosphere of the planet. When these hydrocarbons descend into the lower cooled parts of the atmosphere, they are transformed into ice particles and form haze. Thanks to this process, tolines are formed, giving a red tint.
Up to this point, scientists have argued that the temperature is too high for the appearance of haze at a height greater than 30 kilometers.
“We collect the necessary information to find out what is happening,” said Summers.
In addition, some photos prove that there are some exotic ice on the surface, which tend to "move." And the team did not even expect to find out that such activity was happening quite recently.
The pictures reveal fascinating details inside the Texas Plain, the unofficial name for the Plains satellite, which is located on the west side in the shape of a heart, known as Tombo Regio. There you can see that a layer of ice was floating and perhaps still floating, reminding movement of glaciers on Earth. “We managed to see the surface as well as on such planets as Earth and Mars,” admires John Spencer. “And I can't get enough of it.”
Among other information, there is also evidence that the Plain Satellite is rich in nitrogen, carbon monoxide, methane, and ice.
“Since Pluto’s temperature drops to minus 390 degrees Fahrenheit, these ices can easily flow, recalling the movement of our glaciers,” said Bill McKinnon, deputy head of geology and geophysics at the University of Washington in St. Louis. “In the southern part of the heart-shaped form, located in the dark region of the equator, it seems that this area was the origin of glaciers”.
The mission of New Horizons will continue to transmit data stored in their flight recorder to Earth until 2016. Spacecraft are located 12.2 million kilometers outside of Pluto, flying deeper into the Kuiper belt.
Johns Hopkins University, which houses the Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland, designed and built the New Horizons spacecraft and directs NASA science missions.