It has long been known that contact between galaxies affects the evolutionary process. These are standard events and most often you can see signs of fusion, such as tidal tails and other morphological distortions. The most dramatic collisions cause galaxies to flash in the infrared range, turning them into the brightest objects of the Universe. This brightness allows you to study objects at great distances and set the size of the space.
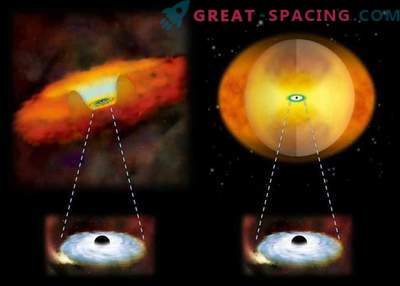
Two processes are responsible for increased radiation: stellar birth and feeding of a supermassive black hole in the galactic center (active galactic core). These are different processes and they are easy to distinguish, but everything is complicated due to dust or the weakness of the galaxy itself. Therefore, researchers have to use the form of a complete galaxy radiation profile from ultraviolet to the far infrared range.

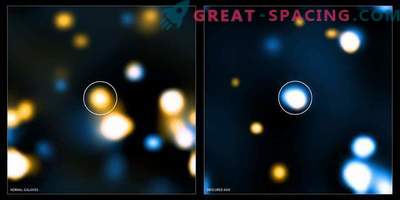
Merging galactic pair VV705. Scientists measured a set of similar objects to calculate the relative contribution to the luminosity from star formation compared to accretion around the core of a supermassive black hole. For VV705 it was fixed that almost 75% of the luminosity comes from a stellar birth of If bursts of stellar birth were responsible for the inclusion of bright galaxies in the early Universe, then many of today's stars may have formed in similar events. But with the predominance of active galactic nuclei, more convex jets and fewer new stars should have been observed. Scientists decided to analyze 24 relatively approximate luminous events of the galactic fusion in order to understand how often and to what extent the activity of the active galactic nucleus is related to energy.
Scientists were able to obtain the most meticulous information SED in 33 spectral bands of the seven missions of NASA. Then they applied the new computational code. It turned out that the contribution of the nuclei reaches 90% of the total luminosity. In other cases, drops below 20%. While the findings are limited due to a modest sample of galaxies in the study. Therefore, the analysis now extends to several hundred merger events to reinforce the findings.