The Japanese space agency JAXA received more than 200 photographs taken by small rovers on the asteroid Ryugu. We have not yet managed to find a smooth surface for the planned landing of the spacecraft in early 2019.

The picture from the JAXA rover-1A, mined on December 13, 2018, shows the surface of the asteroid Ryugu. The Japanese space agency received more than 200 images from two rovers on the asteroid, noting that there are no signs of surface smoothness.
Representatives of the agency reported that two rovers (solar-powered) became inactive and most likely are in the shade. However, they still respond to signals after 3 months, exceeding their lifespan by several days.
In September, the Minerva II-1 rovers were dropped by an unmanned spacecraft Hayabusa-2 onto Ryugu, an asteroid distant 280 million kilometers from Earth. They had to collect surface data. Many photographs show a rocky surface, which is a problem for the planned landing of Hayabus II. He had to be postponed from October, because they could not find a reasonably safe location.
JAXA is said to have narrowed down potential landing sites and still doesn’t give up trying to take asteroid samples. Scientists analyze data obtained by rovers to agree on a safe plan.
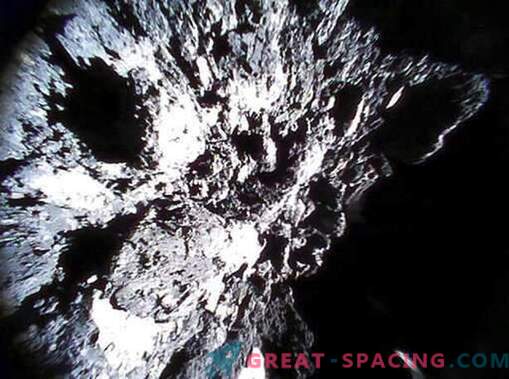
The photograph of the Rover-1A dated October 20, 2018 shows the surface of the asteroid Ryugu. JAXA received more than 200 frames from two rovers on the asteroid, noting that there are no signs of surface smoothness. Researchers believe that one of the rovers drove about 300 m, descending into a place with weak gravity for the vehicle wheels. He managed to get more than 200 photos. His partner sent 40 images and in 10 days stopped moving. Most likely, the problems with the functionality were affected by a lower temperature of the asteroid than expected.
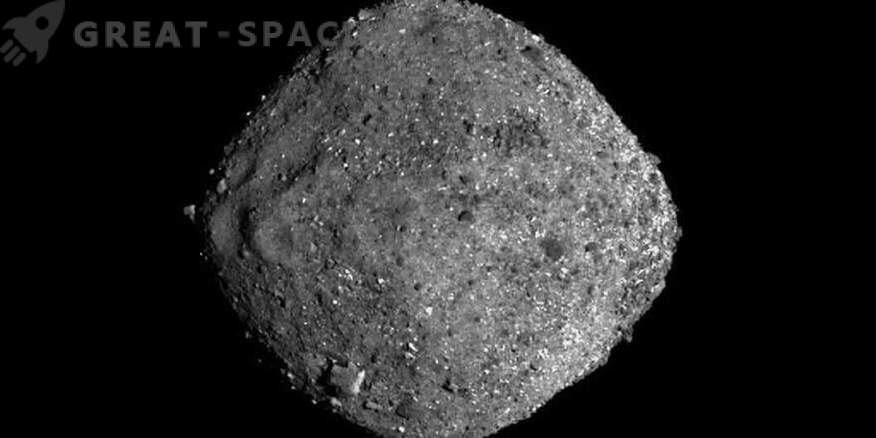
The findings show similarities with the shape and surface of the Bennu asteroid, which is now being monitored by the NASA OSIRIS-REx. The findings suggest that the asteroids are more humid and stronger boulders than predicted. This is one of the oldest objects that can reveal the details of the development of the solar system and the evolution of the Earth.

A photograph dated October 26, 2018 shows the surface of the asteroid Ryugu. JAXA received more than 200 images from two rovers on an asteroid, noting that there are no signs of surface smoothness.

The frame of October 26, 2018 of the Rover-1A shows the surface of the asteroid Ryugu. JAXA received more than 200 images from two rovers on the asteroid, noting that there are no signs of surface smoothness, which greatly hinders the planned landing of the Hayabus-2 spacecraft