Mix water, methanol and ammonia at low temperatures and low pressure, irradiate with ultraviolet light, and what do you get?
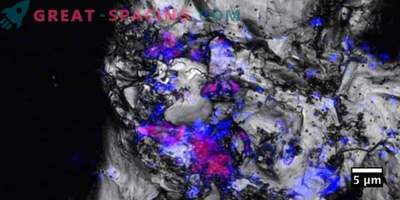
Remains of organic matter, which, when heated to room temperature, contain ribose and other types of sugars, are considered to be the building blocks for RNA and DNA - molecules necessary for the existence of all known forms of life.
The experiment shows that ribose and similarly structured sugars, such as arabinose, xylose and lyxose, can be collected under the chemical and temperature conditions of cosmic ices during the formation of the Solar System.
“Identification of a ribose and a sugar molecule associated with it in simulated cometary ice is a new and completely unexpected discovery,” astrochemist Cornelia Meinert of the University of Nice, Sophia Antipolis, France, Discovery wrote in an e-mail, “relevant to many theories about the origin of life. "
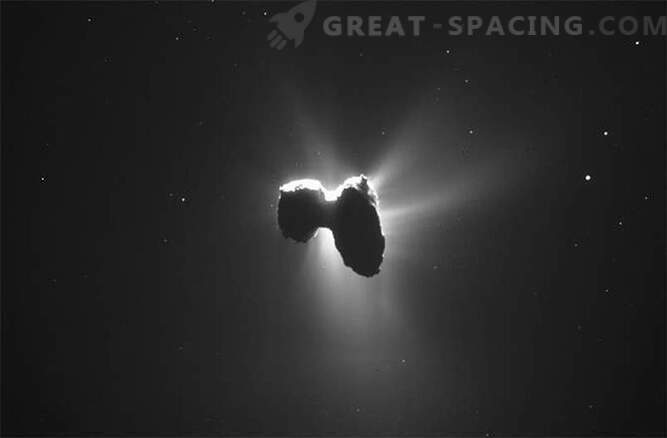
The experiment, reported in Science this week, is related to the work on the development of an organic detector for the comet of the Phil descent vehicle, which was sent by the European spacecraft Rosette to the surface of the comet 67P / Churyumov-Gerasimenko in November 2014. Fila did not find a ribose on the comet, but he discovered three organic compounds that were also in the laboratory samples.
“The detection of ribose is really exciting and gives an idea of the prebiotic origin of the critical connection necessary for life,” said astronomer Donald Brownle of the University of Washington, who did not participate in the study.
“In the first few million years, the outer regions of the solar system contained a large amount of ice covered with dust particles, and the proposed ultraviolet irradiation of these dust particles is certainly an important source of organic materials. It seems that a wonderful gift from nature is a process that can lead to ribose. We could not do without him, ”- writes Brownlee in an email Discovery News.
Scientists do not know how life began on Earth, but many believe that the key components came from comets and asteroids crashing in a developing planet.
“I’m sure that ribose can survive when it enters the atmosphere,” Brownlee added.
“Meteorites are hot on the surface, but not in their depths. If they are rock materials, they are similar to Baked Alaska (dessert). It is likely that some cosmic dust particles from comets may also carry ribose through the atmosphere. It is very interesting, whether the Earth can create ribose and other critical molecules or they should come from somewhere else. Irradiation of frozen volatile matter is a natural process in space, but this is not so easy on Earth, ”said Brownlee. Meinert and her colleagues do not yet know the exact mechanism that led to the formation of ribose and other sugar molecules in simulated ice.
“Previous attempts to find sugar molecules in simulated ices or meteorites failed due to analytical constraints,” she added.
Further studies are planned on the structural asymmetry of sugar molecules, or chirality, in the hope of learning more about the evolution of DNA.
Meinert would also like to look at the ribose in meteorites and in asteroid samples that are to be delivered to NASA by the upcoming OSIRIS-REX and Japanese Hayabus-2 missions.