Scientists managed to find a new radio galaxy TGSS1530 with a high redshift (5.72). This suggests that before us is the farthest radio galaxy of all discovered.
It is known that radio galaxies with a high red shift (one of the most massive) contain a huge amount of dust and gas. Often they live in the center of clusters or protoclusters. Their study will make it possible to take a fresh look at the creation and evolution of large-scale ecumenical structures.
Radio galaxies attract special attention, whose redshift index exceeds 6.0, which leads to the epoch of reionization - the early stage of the evolution of the Universe, during which the cosmic gas went from neutral to ionized. Such radio galaxies can be used as unique tools for a detailed study of the reionization process.
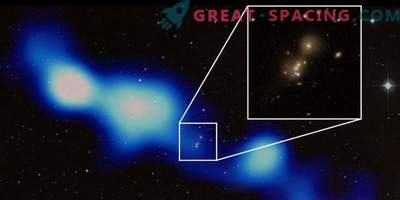
Enhanced y, J, H and K images from the UKIDSS large-scale 1.4 GHz survey for TGSS1530
Recently, researchers have noticed a new radio galaxy in the alternative release 1 (ADR1) of TGSS data. To confirm the discovery, they observed it in April 2017 using Gemini multifunctional spectrographs (GMOS). In February and May 2018, the LBT camera in the infrared region of the Large Binocular Telescope (Arizona) was used for the review. The analysis showed that TGSS1530 covers about 11,400 light-years, which is typical of high-redscip radio galaxies. It resembles radio galaxies with a redshift of more than 4.0. It is believed that a high figure and relatively small radio and Lyman-alpha dimensions may indicate that we are in front of a radio galaxy at an early stage of its evolution. In addition, the TGSS1530 radio frequency, calculated at a frequency of 150 MHz, is 29.1 W / Hz (the brightest in its era).
Despite the high redshift, this radio galaxy can move from the pedestal due to future research into more powerful devices like LOFAR.