C / 2016 R2 (Pan-STARRS) is a comet rich in carbon monoxide and not containing hydrogen cyanide. This was reported in a new study conducted by scientists from the University of South Florida.
Opened on September 7, 2016, C / 2016 R2 is the Oort Cloud comet orbiting the Sun at a distance of 740 a. e. for 20,000 years in a highly eccentric orbit. It is known that endowed with a dark blue coma and an extremely complex ion tail.
Scientists consider the Cloud Oort as a repository of cometary nuclei containing the ice from the early system. Therefore, the study of such objects provides valuable information about the origin and formation of planets and other celestial bodies orbiting the sun. C / 2016 R2 was celebrated in December 2017 and January 2018 using a 10-meter sub-millimeter telescope at the Arizona Radio Observatory. The observational campaign focused on the search for emissions of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen cyanide (HCN).
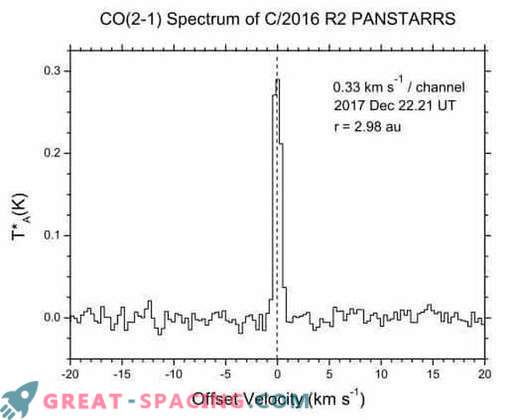
The first detection of CO emissions in C / 2016 R2 at UT on December 22, 2017, when the comet was at r = 2.9 and ∆ = 2.1 a. e As a result, it was possible for the first time to fix neutral carbon monoxide in a comet. It turned out that the rate of CO production is extremely high compared to other comets and half as much as in C / 1995 O1. Now C / 2016 R2 is described as a CO-enriched comet, in which the release of carbon monoxide is considered the main engine of activity.
But scientists also found that the rate of production of hydrogen cyanide is significantly lower - 100 times less than that of C / 1995 O1 at the same distance. If you use a typical understanding of cometary compositions, it is difficult to understand the chemistry of C / 2016 R2. To understand this feature, astronomers measured the rate of molecular nitrogen production. It turned out that the comet is also rich in N2, which does not agree with the typical situation of nitrogen depletion.
Estimates emphasize the strangeness of C / 2016 R2. Further observations will make it possible to understand why it is different from others.