Radar images from NASA’s Martian orbiter show that the Red planet has gone through climate change cycles. And now it is a process of melting.
Mars is in the process of a 370000-year climate shift that one day will make the Red Planet warmer. This is indicated by new research.
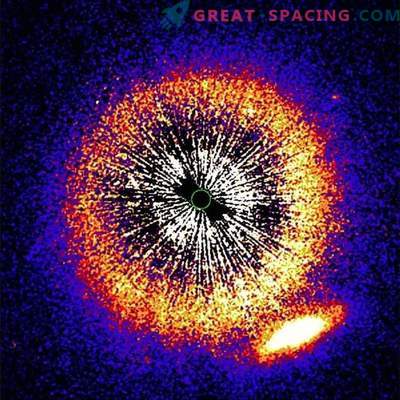
Evidence that Mars is coming out of the ice age comes from analyzing radar images showing dramatic changes within the ice layers inside the planet’s northern polar cap. As the planet warms, more ice gathers in its polar regions. That is, unlike long-term climate change on Earth, here everything happens in the reverse order. Cycles are caused by variations in the orbits of the planets around the Sun and their axial tilts.
During the Ice Age of Mars, most of the ice is collected at lower latitudes.
“It will change the overall color of Mars, that is, make it more white,” planetary scientist Isaac Smith of the South-West Research Institute in Boulder, Colorado wrote in a DNews e-mail. “I can confidently say that even people on Earth will notice a color change. This ice will remain there until the end of the ice age, until it becomes unstable. It then shifts to higher latitudes, mainly to the poles, ”said Smith.
Since the end of the last Ice Age of Mars (approximately 370,000 years ago), about 21,000 cubic miles of ice has accumulated mainly around the planet’s north pole. It shows an analysis of radar images taken by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
This is equivalent to about 2 feet of ice evenly distributed over the entire surface of the planet.
A study published in Science this week is the first to provide statements about the amount of ice moving around the planet. This is information that will help researchers put together the climate history of Mars.
Climate research is the key to finding out when Mars (the planet most resembling Earth in the solar system) could be best suited to life.
“We have a volume of ice (after the ice age), which can now be used for direct climate models. Previously, these models were based on guesswork, ”said Smith. For the first time, scientists directly linked a certain layer of Martian ice with a specific period of time.
“In the end, we would like to be able to do this for each layer, so this is a step in the right direction,” Smith said.
Understanding the history and evolution of Mars’s climate helps scientists see which processes (such as dust storms) play an important role in determining temperature and surface conditions, says Christine Hvidberg, an assistant professor at the Center for Ice and Climate at the University of Copenhagen.
“It is also important to understand that Mars is actually going through changes now ... This is a very important step towards understanding the climate on Mars,” Hvidberg said.