This is a massive galactic cluster of Abell 2744, captured by the Hubble Space Telescope. You can consider one of the youngest and tiny galaxies in space.
A new study from the Australian National University and the University of Sydney showed that as the galaxies age, they become larger and increase the amount of dust.
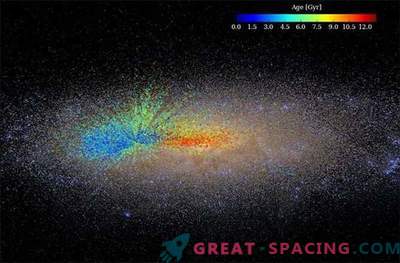
The stars in a young galaxy are moving in an orderly manner around the disk. Therefore, initially all galaxies resemble flattened spheres. But as “growing up” becomes swollen, because the stars move in all directions. The age of the Milky Way is more than 13 billion years, so it can no longer be called young. However, the galaxy is still endowed with a central bulge of ancient stars and spiral arms of young objects. To develop a galactic form, the researchers measured the motion of stars with the SAMI tool on the Anglo-Australian telescope at the Siding Spring Observatory. They studied 843 galaxies of all kinds.
The analysis showed that it was not obvious that there is a connection between form and age. Therefore, nature may indicate a deep basic relationship. It is important to remember that as the galaxies develop they collide, which is why the stellar motion is disturbed. Age is measured through light. Young stars are initially blue, and in old age they turn red.
Scientists have long known that age and form are connected in very extreme galaxies — extremely flat or round. But for the first time it was possible to show this connection for all galactic species (of all forms, ages and masses).