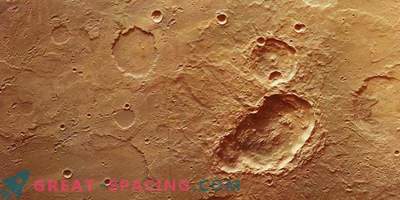
HiRISE image from the MRO orbiter shows a shock crater with a landslide caused
In 2006, the NASA MRO orbiter was fixed on the Mars orbit. Using a wide range of scientific instruments, including cameras, radar and spectrometers, this device has been analyzing for many years reliefs, minerals, geology and ice on the Red Planet, helping other missions. The project was designed for 2 years, but remains in operation for the past 12 years.
Then the MRO played the role of a relay for other missions (transmitted data to Earth). Recently, we managed to fix a shot of the impact crater, which caused a landslide, which left a long dark line along the wall. Such bands are formed when a dry layer of dust collapses down the edge of a Martian hill.
They differ little from current sloping lines (RSL). These are areas where seasonal dark stripes appear on the slopes on warmer Martian days. They are believed to be caused by streams of salt water or naturally falling dry dust grains. But in a particular case, the dust set in motion due to the impact of a meteor. It is believed that the impact that formed the crater happened about 10 years ago. The crater itself covers 5 m, but the line is pulled out to 1 m in length.
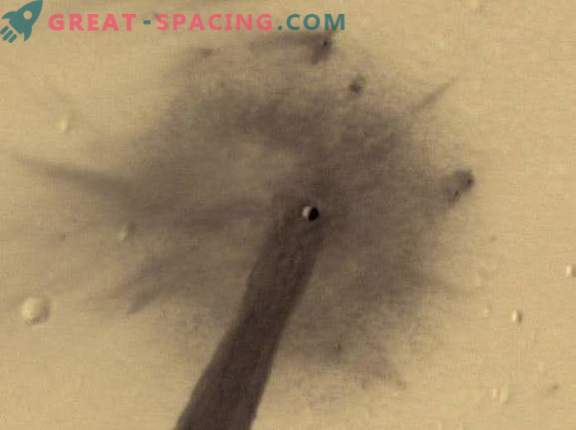
Approximate view of the crater. Performed by HiRISE on MRO
The picture was obtained by the scientific tool for visualization of high-resolution image HiRISE, which is controlled in the Jet Propulsion Laboratory The device provides daily reports on the weather and surface conditions on the Red Planet, examining potential landing sites for future spacecraft.
MRO now has enough propellant to function until the 2030s. Given the value to explore Mars, it is likely to be used to the last drop of fuel. Will he still work when the first cosmonaut sets foot on the Red Planet?

Wide-angle view of the impact crater captured by HiRISE on the MRO