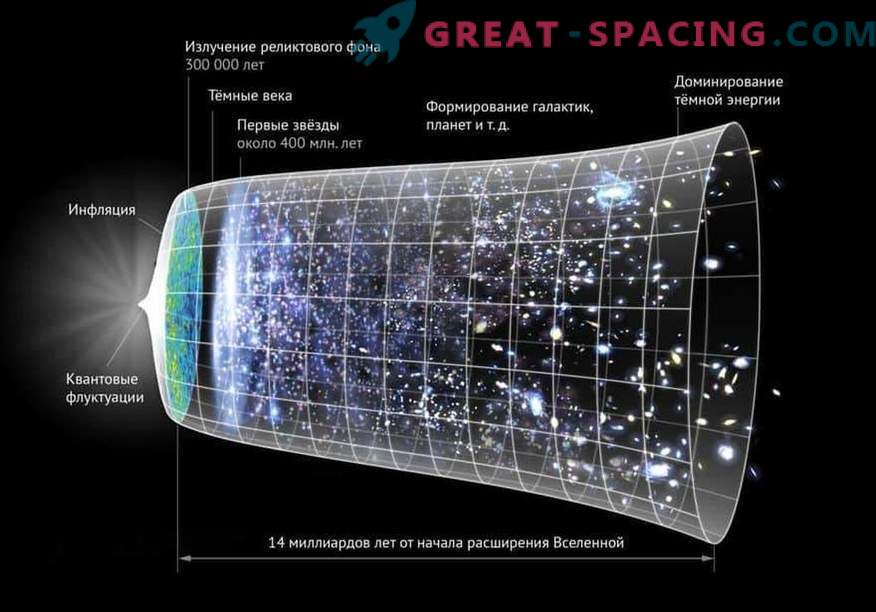
Artistic interpretation of mechanical expansion of space. Look for the left side, where expansion occurs during the inflation period, and acceleration is noticeable in the center.
Scientists have created a model of events that followed the Big Bang in order to better understand the process of star formation. The emphasis is on massive explosions that controlled the process of creating galaxies. And they continue to influence today.
The results confirm the old theory of supernova explosions and the fact that they slow down star formation.
Blast Waves
Scientists from Edinburgh say that supernovae create powerful gusts of wind that slow down the rate at which gas used by new stars flows into the galaxy. To recreate the dark matter, hydrogen and helium, created after the Big Bang, used a supercomputer. They compared them with the amount of hydrogen around the galaxies. Scientists have noticed that the level of hydrogen outside the galaxies is higher than expected, and strong winds slowed down the gas flows.
Black Hole Effect
But the simulations could not reproduce the amount of hydrogen around the most massive galaxies, inside of which there are quasars (hold a lot of energy). Scientists believe that quasars can influence even more than supernovae, since they form giant gas jets, supported by black holes.
It is still incredibly difficult to identify all the mechanisms of the galactic formation process, but scientists are on the right track.