20 years have passed and the record of the most distant radio galaxy has been broken. Scientists managed to find a radio galaxy at a time when the Universe reached only 7% of the present age at a distance of 12 billion light years. The team used the GMRT radio telescope (India) to initially identify the radio galaxy. The distance was then calculated using Gemini (Hawaii) and the Large Binocular Telescope (Arizona), measuring the redshift.
The red shift at z = 5.72 means that the galaxy is perceived as it looked at the time of the universal age of a billion years. That is, its light is almost 12 billion years. The red shift measurement reveals the distance. The farther the galaxy, the faster it moves away from us. Therefore, the light becomes more red, due to the Doppler shift. So, the higher the removal rate, the greater the redshift.
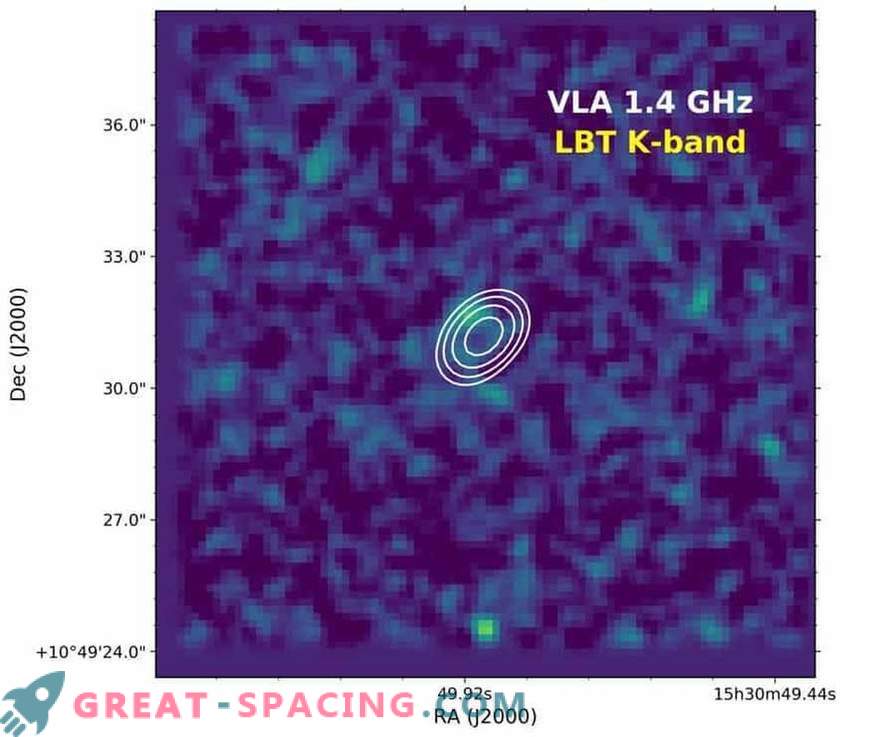
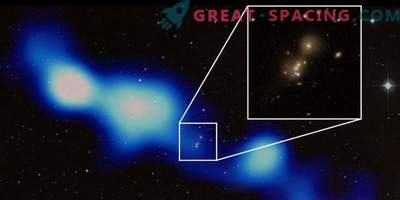
The image shows the near infrared region in the K band, obtained using the Large Binocular Telescope (Arizona) with radio emission (white). The fact that the galaxy was not detected at infrared wavelengths from which the radio emission originates helped to independently confirm its record distance Radio galaxies are rare objects in space. These are colossal galaxies with a supermassive black hole in the center, which actively absorbs gas and dust from the environment. This activity initiates the launch of high-energy jet streams capable of accelerating charged particles around a supermassive black hole almost to the speed of light. These jets are clearly visible on the airwaves.
The fact of the existence of such galaxies in the distant Universe surprises astronomers and plays an important role in understanding galactic formation and evolution. Their detailed study also sheds light on the creation of primary black holes that control and regulate galactic growth. The previous record was a radio galaxy with a redshift of z = 5.19, discovered in 1999. The next generation of radio telescopes in combination with the world's largest optical and IR telescopes will be able to detect radio galaxies with an even greater redshift.