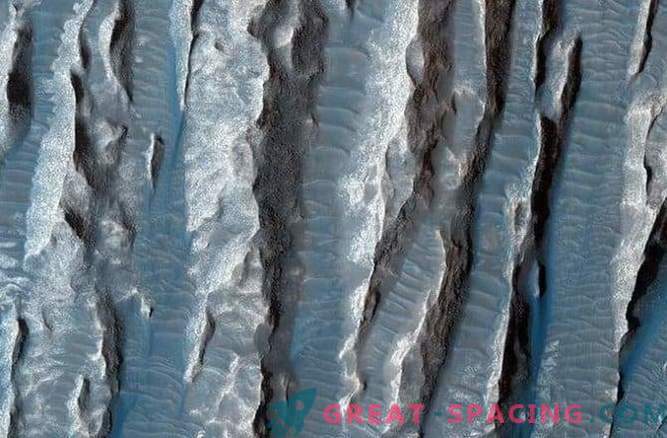
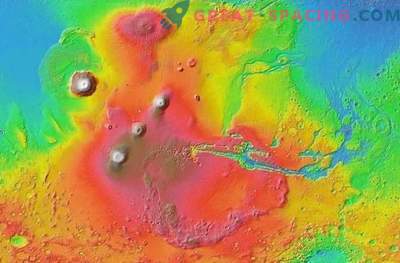
These bluish stone fingers on the surface of Mars are called hollows. These are the remains of rocks that turned into long, skinny fingers, since they were sandblasted by particles under the influence of the wind. These unusual formations are located in a frozen, windswept desert located in the Mars area called Arsinoes Chaos. Arsinoes Chaos is a giant, 4000 kilometers long, 7 kilometers deep, part of a canyon south of the Martian equator, in the far east of the Marineris valley.
This massive canyon, which stretches for a quarter of the way around the planet, is considered to be a huge rift valley created by the tectonic fracture of the Martian crust due to its compaction billions of years ago.
Water and wind erosion subsequently further expanded the canyon system, leaving a deep imprint across the surface of Mars.
Scientists believe that this is the mixed relief of the Arsinoes Chaos at the base of a canyon formed by massive water floods cutting out the exhaust channels that originated in this area, after which the water flowed north to the Martian northern lowlands that were the seabed of the ancient ocean. Gray and blue perpendicular sandy wavy dunes between hollows are called transverse aeolian ridges.
Eolian ridges occupy about half the height between sandy dunes formed by jumping sand and waves formed by splashing sand particles.
The picture was taken by a HiRISE camera installed on a NASA spacecraft called the MarsReconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) on January 4th.
MRO makes a complete revolution around Mars in the nearest polar orbit 12 times a day at an altitude of about 300 kilometers.
The spacecraft has been in Mars orbit since March 2006, completing the first two years of the main mission, the MRO is now on its fourth mission. On February 7, the MRO made its forty-thousandth turn around the red planet.
Orbitor has already shown that Mars is a much more dynamic and diverse world than previously thought, with some regular warm season, reminiscent of water flow, which provides convincing evidence of the presence of liquid water on the red planet today.