The winter sky is the favorite thing for astronomers. Darkness in the beautiful frosty weather best provides the clearest sky for a long time without a single cloud. I have several significant reasons to love winter, so I hope they will inspire you, and maybe soon you will go out under the open sky at night and enjoy it.
Andromeda Galaxy
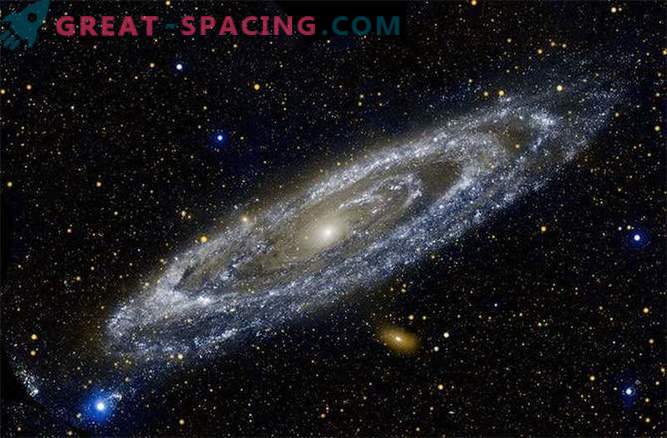

First of all, Andromeda. It can usually be seen in the autumn period in the neighborhood of another galaxy in the west during sunset. If you are in a dark place, you can easily find it in the sky with the naked eye. To do this, look at the area of the Great Pegasus constellation and find the topmost star, which is usually located in the upper left corner of the constellation known as Alferathz.
From here you can notice two faint stars. The second was called the Mirage or "right turn". At this point, you need to "scan" the sky through binoculars. Look for something like a drop of water, this is Andromeda Galaxy. It is located more than 2 million light years from us. This fact means: the light that you can see with your own eyes travels over 2 million years. In other words, you look into the past! A low telescope approximation is the best way to observe the galaxy.
Orion Nebula

East of Pegasus is the well-known Orion constellation. If you want to find him, then you should be able to identify his famous three stars in one zone (from east to west: Alnitakom, Alnilam and Mintaka) from the central star to the beginning of the fall of the imaginary horizon line. At first, you will see several blurry stars just below the belt; they are the center of interest to scientists. For the naked eye, the Orion Nebula looks just like a fuzzy drop, but using binoculars you will notice some real signs of the nebula. The best views today are visible through a low-power telescope. The larger the diaphragm, the brighter the image you will see. Carefully study the center of the nebula and the cluster of stars. It focuses only young stars, formed from a hot cloud of gases at a distance of just over 1300 light years from us.
Sirius

Sirius is a very big star. You should watch her not only because she is beautiful, but also because she has a strange dog shape. Because of this, she was nicknamed "star-dog." Sirius is a double star. You can find it at any time during the winter in the northern hemisphere.
However, good weather conditions and an aligned telescope are irreplaceable things. To test your observation skills, try to distinguish between Rigel and a companion star, which is comparable to its brightness. Rigel A is whiter in color and is located in the lower right corner of Orion. If you can complete this task, then consider that it’s not so bad in my observations, since I see the difference between Rigel A and Rigel B. Before starting to admire, I advise you to choose a well-viewed place in advance.
Jupiter
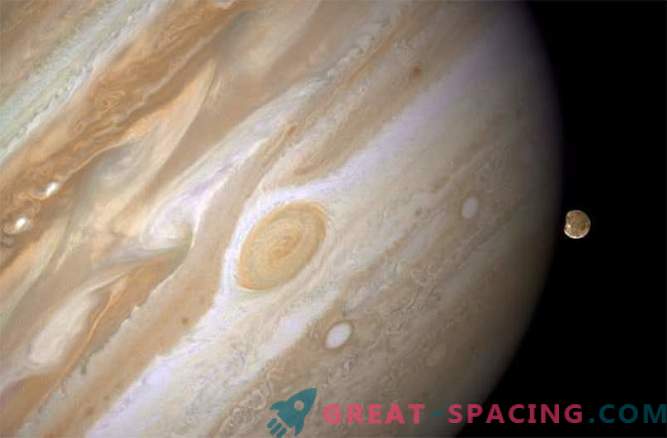

This winter Jupiter will be beautifully placed in the night sky on the border between the constellations Leo and Virgos. Powerful binoculars may be able to detect four Galilean satellites, but not a fact. The telescope will cope with this task many times better. Look through it for a certain period of time during one night and track the movement of satellites around the planet before giving all your attention to her. A magnification of 100x and above will be able to reveal to your eyes the many belts surrounding the planet. And if the timing is right, then the Great Red Spot will be located next to Jupiter. This is a hurricane raging for several hundred years.
Mars

Immediately after Jupiter, the size is Mars. Because of the orbital periods, Mars and Earth come closest to the minimum distance every two years. This year the position (when Mars appears on the other side of the sky towards the Sun) is not the best, but it will still be better than the positions of previous years.
You need the telescope in order to get a high level of detail on the Martian disk, but the function can be greatly enhanced by using red and orange filters. These filters will enhance the brightness of the polar caps, darkening the surface of Mars. By observing in this way you can identify all the irregularities of the dark rocks of the planet.