Coronal mass ejection
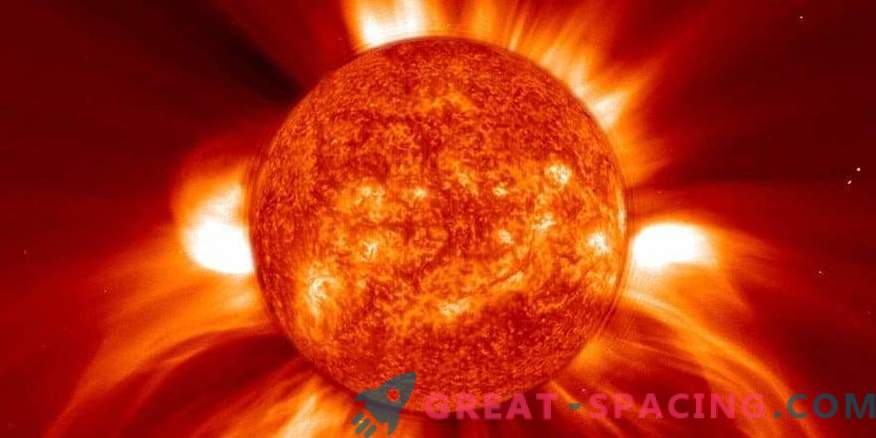
This week, ESA (European Space Agency) is celebrating the dynamic phenomenon of space weather. It is difficult to realize the size and power of our Sun - a giant ball of hot gas with an age of 4.6 billion years and 1.3 million times larger than the Earth.
Unpredictable and temperamental
In space, this bright glowing star plays an important role, dominating the environment in the solar system. This is an unpredictable and very temperamental star, giving life to our planet, but taking it away from others. It is all about intense radiation and a combination with an enormous amount of energetic material emitted in all directions. All this is space weather.
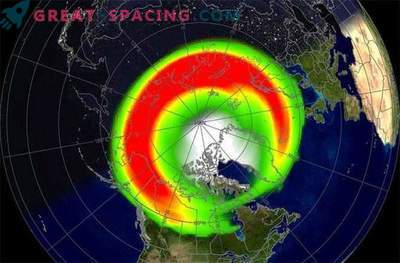
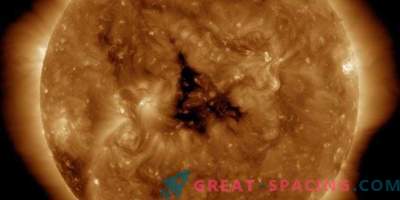
If everything is so bad, then how did earthly life survive? It is necessary to thank our magnetic field that protects the planet from the solar wind - a constant stream of electrons, protons and heavier ions from the Sun and coronal mass ejections (random flashes of the Sun and the release of billions of tons of solar plasma into space). These outliers are trying to penetrate our defenses, and all the while creating geomagnetic storms.
Serious problems for modern life
These storms can cause serious problems for modern technological systems, destroying and causing damage to satellites in space, as well as damaging navigation, telecommunications, electrical networks and radio communications. There is also a radiation hazard for astronauts in space on the ISS, the Moon or Mars. These events cannot be stopped, but an early warning of an impending solar storm will give satellite operators, power grids, and telecommunications systems time to take protective measures.
Solar hazard study
Therefore, the Lagrange mission is being developed at ESA to support an early warning system for “solar behavior”.
Observing the Sun from a unique position in space, Lagrange will track potentially dangerous sunspots and high-speed solar wind streams before they get to Earth. The mission data will go to the ESA Space Meteorological Service Network to generate warnings and forecasts.
Protective measures against space weather are becoming an increasingly important project, since most of humanity is increasingly dependent on space services and technology every day. In 2019, this topic will be discussed at the ESA Council of Ministers.