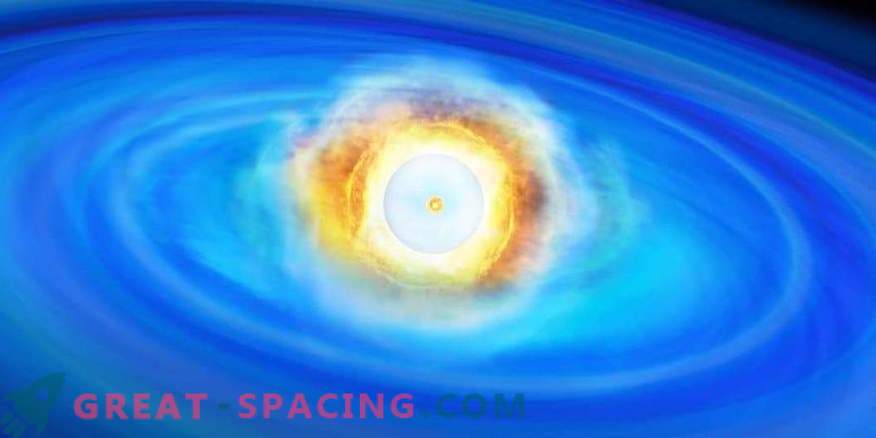
Nuclear detonation of the surface helium layer led to an internal shock wave. This caused a carbon fusion in the center.
Scientists have noticed evidence that the brightest stellar explosions in space can be created by nuclear helium detonation near the surface of a white dwarf.
We know that certain stars end their existence with a huge supernova explosion. Massive objects are becoming famous, but white dwarfs also explode. This happens if they are part of a binary system. A white dwarf takes away material from a neighbor and brings himself to the type Ia supernova explosion.
Due to the uniform brightness (5 billion times brighter than the Sun), this type is used to calculate spatial distances. But researchers are still trying to figure out the explosive mechanism. It is also surprising that such events occur every century in any galaxy. Japanese scientists decided to study this question. To increase the chances of detecting Ia-type supernovae in the early stages, they used the Hyper Suprime-Cam on the Subaru telescope. As a result, the team created a system to automatically search for a specific type of supernovae.
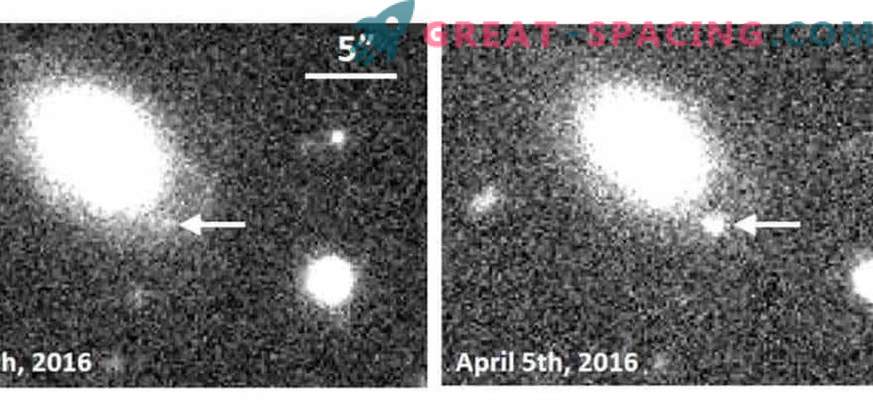

Image taken from the Subaru Hyper Suprime-Cam Telescope
Just imagine that in one night they managed to fix 100 candidates for Ia-type supernovae, including one that exploded a few days ago. Hence the idea with a helium layer. Its ignition activates a chain reaction and leads to a stellar explosion. This is confirmed by the model on the ATERUI supercomputer.
This is the first step in the global understanding of type Ia supernovae. The team will continue to study the remaining candidates in order to better consider the events immediately after the explosion.