The Mars-Express webcam has managed to create a catalog of 21,000 images, proving its value as a scientific tool for the global study of unusual high-altitude Martian clouds.
Initially, a low-resolution camera was installed to visually confirm the separation of the Beagle-2 landing module in 2003. In 2007, it was turned on again to connect the public to the study of the planet.

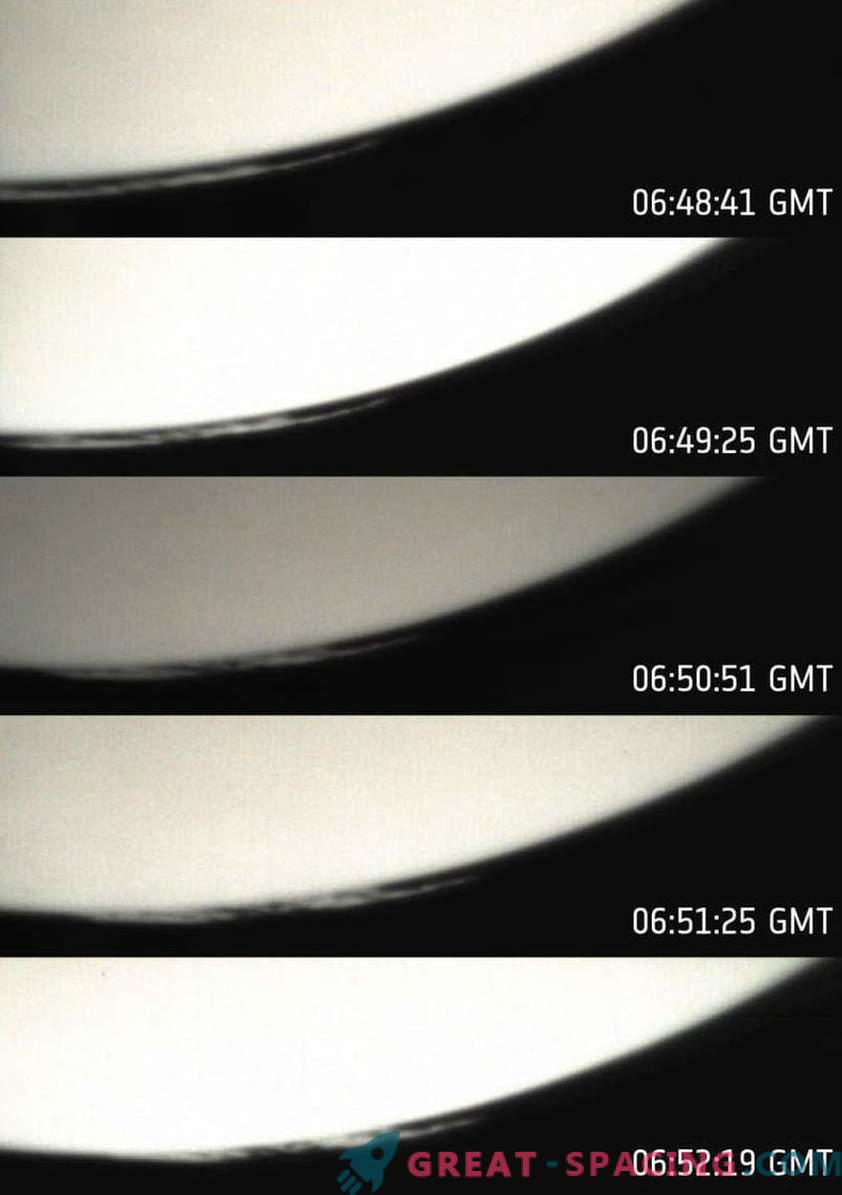
The sequence of frames obtained by the Mars-Express visual observation camera on March 7, 2014
Last year, the camera received new software and became an additional scientific instrument. With its help, it is possible to consider an amazing cloud cover. Of course, you can use other tools or spacecraft for this, but it is the webcam that provides a global overview. The data obtained help to understand the atmospheric phenomena.

Pictures are mined on December 15, 2009
Between 2007 and 2016, a catalog of 21,000 images was created, where 300 are set aside for specific studies. Cloudy features extend in a radius of 50-80 km and extend horizontally at 400-1500 km. To understand the cloudy nature (dust or ice particles), the scientists compared the photos with the predictions of atmospheric properties, described in detail in the climate database of Mars. Also studied shots from the MRO. Most studies state that clouds are represented by water ice.

Dusty Clouds over Mars
Clouds with high ice concentration depended on the solar position: can be detected at dawn and at the beginning of the day, when the temperature mark is lower. With increasing light, they dissolved.
Variations in cloud cover are also affected by changes in temperature, season, and atmospheric dynamics. One of the events was associated with a local dust storm in the northern hemisphere. The storm covered 1950 km on the outer edge and 730 km on the inner edge with a width of 60-130 km.
Among the examples it is worth remembering the cloud recorded on December 15, 2009 above the equatorial line. It is located at an altitude of 40 km and covers 830 km horizontally. Interesting features in the form of droplets created by meridional winds were observed.