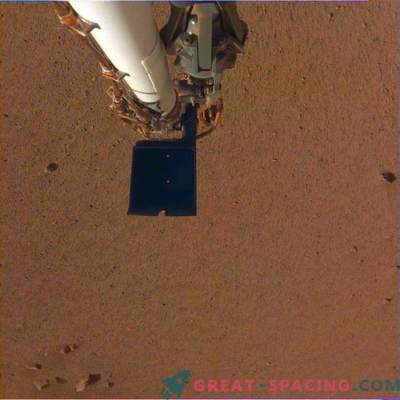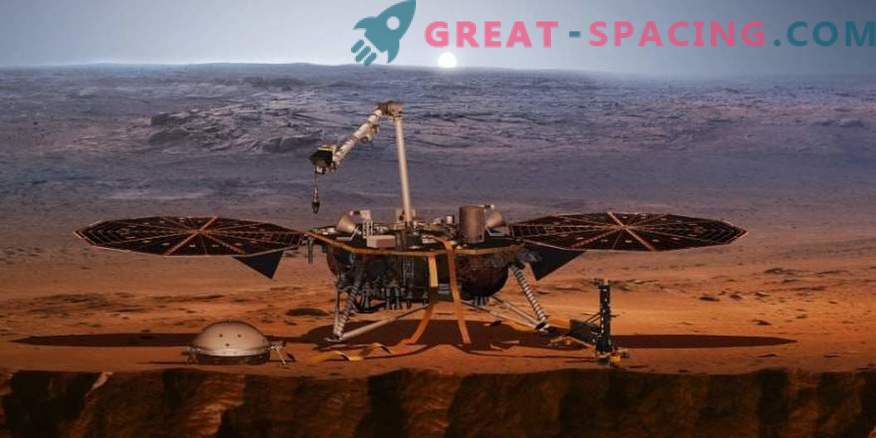
Illustration of the InSight landing pad on Mars. The device is designed to monitor shocks on the surface of the Red Planet.
On May 5, NASA launched a landing gear for Mars InSight. His goal is to study shakes on the Red Planet before possible colonists go there. The launch was made from the Air Force base Vandenberg (California) on the Atlas-5 rocket.
The project, valued at $ 993 million, is aimed at increasing knowledge about internal Martian conditions. If everything goes according to plan, then InSight will overcome 485 million km of flight and arrive at the place on November 26. Experts already know that on Mars there are shakes, avalanches and meteoric impacts. But so far there is no exact data on how frequent these phenomena are and whether there is a threat to the settlers.
French seismometer
The key instrument is the seismometer created by the French space agency. After landing on the Martian surface, a robotic arm is activated, which will set the device on the surface layer.
Perhaps this is not the ultimate goal for InSight, but very important, because it will be possible to hear the heartbeat of Mars. The second tool is a self-clamping probe that will control the heat in the bowels of the planet.
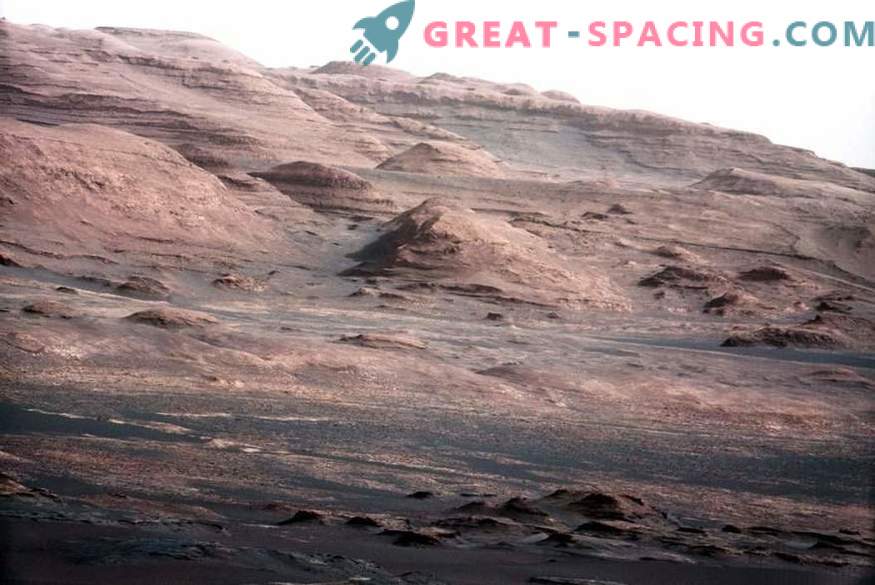

View of the Gale Martian crater, obtained by the Curiosity rover on October 25, 2017
The device was created by the German Space Agency with the assistance of the Polish Space Agency. The probe should go deeper by 3-5 meters (15 times more than in the previous mission). Understanding the Martian temperature is important for sending people in the 2030s. It is expected that the temperature mark at the landing site of the InSight will reach from -100 ° C to -20 ° C. Daytime summer temperatures near the equator can rise to 20 ° C and drop to -73 ° C.
Two Earth Years
Battery consumption and the use of solar are designed for 26 months of work, during which 100 shocks should be recorded. Initially, the device was supposed to start in 2016. But we had to postpone the launch, as the temperature tests revealed a problem with the seismometer part.