ASIM on Columbus
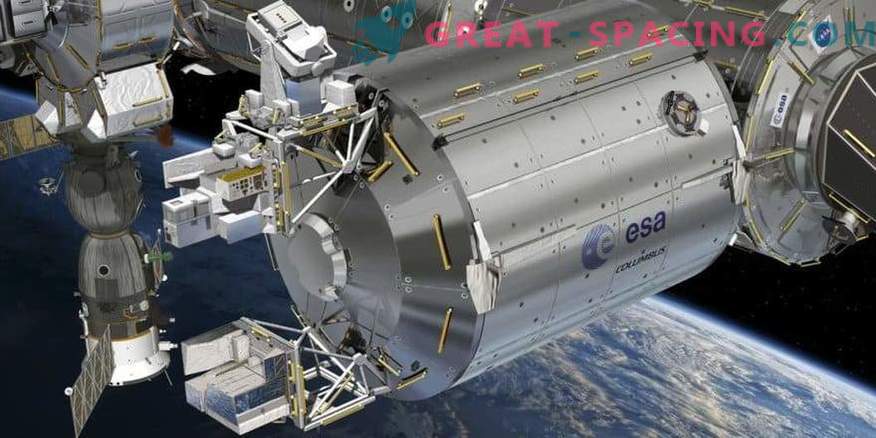
On April 16, ASIM (Atmospheric and Outer Space Monitor) was installed outside the Columbus European Space Laboratory on the ISS. Operators in Canada ran a 16-meter robotic arm to transport a 314-pound object from the Dragon ship's cargo hold to a place on the module.
With a direction to Earth, ASIM will be able to track lightning and powerful electrical bursts in the atmosphere occurring over thunderstorms. Scientists still do not know the mechanism of functioning of these amazing natural forces. The ISS offers an excellent location for gathering information (the station is located at an altitude of 400 km on Earth).
Setup
The first part of obtaining information is checking communication channels. ASIM must send information across the ISS network to a ground station in White Sands (USA), and then to a station in Houston and the Columbus Control Center. The observatory has two sets of instruments for capturing optical images in IR, UV, X-ray and gamma detectors. Sensors will measure light levels. While at installation of levels are guided by a trial and error method. If you set the trigger too low, you get a lot of useless frames.
The visual cameras will determine the necessary areas, and the photomultipliers will be engaged in fixing the details of transient luminous events. Also connect and other sensors that will receive more information about earth gamma flashes.
Each ASIM element is activated alternately and checked to ensure proper functioning. It will take about 6 weeks to check.