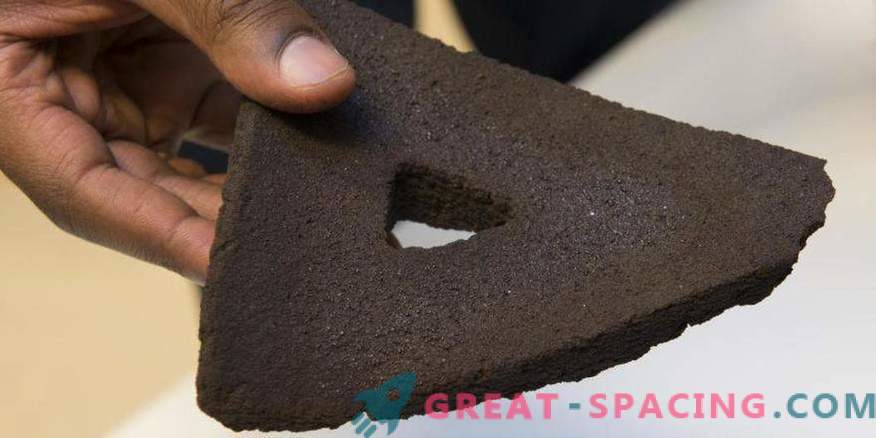
A 3D brick made from moon dust using focused sunlight.
With the help of simulated moon dust and concentrated sunlight, it was possible to create 3D bricks. By this, scientists proved that future lunar colonists could use a similar technique for building settlements on the satellite.
For this, you need a 3D printer that creates successive layers of lunar dust of 0.1 mm at a temperature of 1000 ° C. The formation of one brick (20 x 10 x 3 cm) takes 5 hours. Simulated lunar soil based on the treated terrestrial volcanic material was used as a raw material.
The solar oven at the German Aerospace Center in Cologne has two installations. 147 curved mirrors direct sunlight into a high-temperature beam that allows the material to melt. True, the weather can fail, so instead of the Sun sometimes use an array of xenon lamps.
Of course, on some bricks you can notice weak bends, since some edges cool down faster. Now the team is trying to correct this defect by increasing the print speed. The project proves that lunar construction is no longer a theory. The technology can be used for the RegoLight project in the Horizon 2020 program. The demonstration took place under terrestrial conditions, but the astronauts will have to face the moon: vacuum and high-temperature extremes. The previous project required the presence of salt, but here you just need to ship the printer and solar concentrator to the satellite.

Solar oven in the German Aerospace Center.
The representative of the European Space Agency Tommaso Gidini said that this is an incredibly important technology, as it allows to manage lunar resources. But on Earth, it will be able to ensure the rapid construction of emergency shelters during disasters, which will eliminate the problems of delays in the delivery of materials.
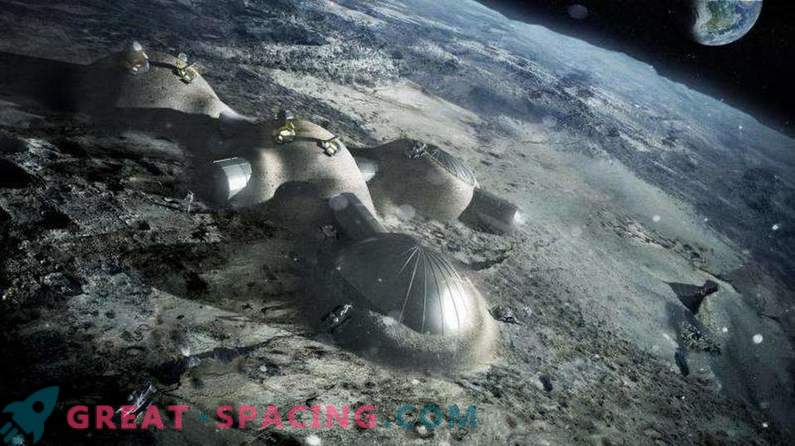

A multi-domed lunar base based on the idea of 3D printing. Inflated domes are covered with a layer of 3D printed lunar regolith, which will help protect against cosmic radiation and micrometeorites.