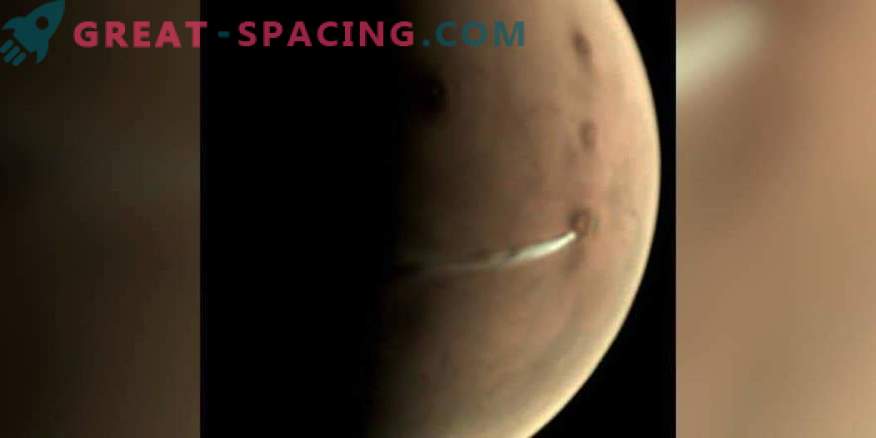
On October 10, 2018, the Mars-Express camera captured an elongated cloud over Mount Arcia on Mars
On the leeward side of the Martian volcano, Arsia was noticed by a mysterious white formation extending for 1500 km. Unlike other cloud structures, which seem puffy and exist for quite a short time, the trail over Arsia was noticed from September 13 and continued to be fixed on November 12.
Mountain clouds are a common phenomenon on Mars, but in the specific case of scientists interested in the length and duration. Volcanic activity was immediately removed from the list of reasons, because Arsia remains calm for more than 10 million years, and peak activity took place about 150 million years ago. The mountain stretches to a height of 20 km and acts as the most southerly volcano of a group of three ancient volcanoes.
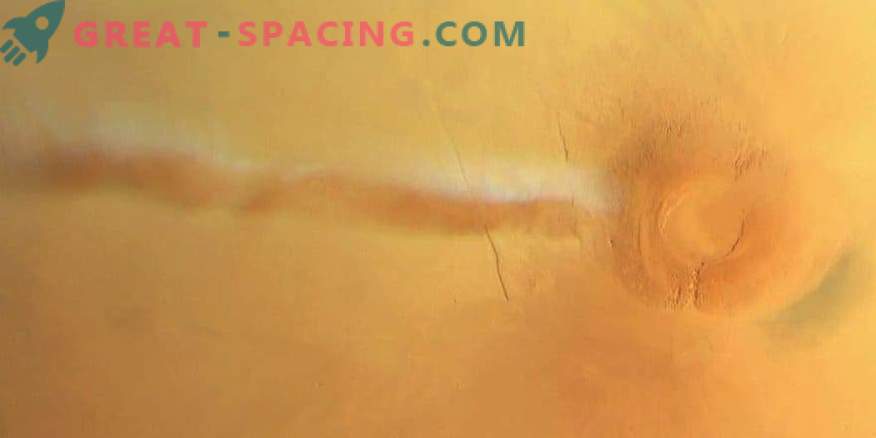
High-resolution stereo camera on ESA Mars Express showed a curious cloud formation on September 21, 2018
The development of the cloud plume is due to a combination of factors that are found in the mountainous regions of Mars and Earth. The main ingredients are pulverized and cool air. Photos of the plume were obtained after a global dust storm finally captured Mars. Dust storms create dark conditions, reducing the amount of incoming heat and increasing the absorption of solar radiation. When warm air meets a topographic feature, like a mountain or an ancient volcano, a disturbance in the air is created.

Elongated cloud over Mount Arcia on November 12, 2018
Given the conditions, the ice particles are not sublimated. As a result, the cloud for a long time transports water ice, which is constantly updated by wind. But why is the Martian plume so steady? Most likely, the whole thing in high humidity. The more humid the air, the more likely that such a cloud is able to renew on the leeward side of a volcano. Probably, before meeting with the volcano, the air was supersaturated with water vapor, so that once condensed water ice could not sublimate.
Why are there no such formations in the north near other volcanoes? Because the northern hemisphere only enters the winter solstice and there are fewer clouds. But summer begins on the territory of Arsia.