After the death of legendary cosmologist Stephen Hawking, researchers continue to make important discoveries about the evolution of galactic clusters. An international team from Taiwan, Italy, Japan and the United States revealed a new fundamental law that provides for the evolution of clusters of galaxies.
Galactic clusters are the largest celestial bodies in the universe. But it was difficult to accurately measure their size and mass, because, for the most part, they are represented by dark matter, which cannot be directly observed. One of the methods of indirect observation is the use of the effect of gravitational lensing, based on Einstein's theory of relativity. Light rays from the galaxy behind the cluster stretch under the action of gravity. If you can measure the shape distortion for many background galaxies, then you can determine the gravitational field of the cluster, and then its mass and size.
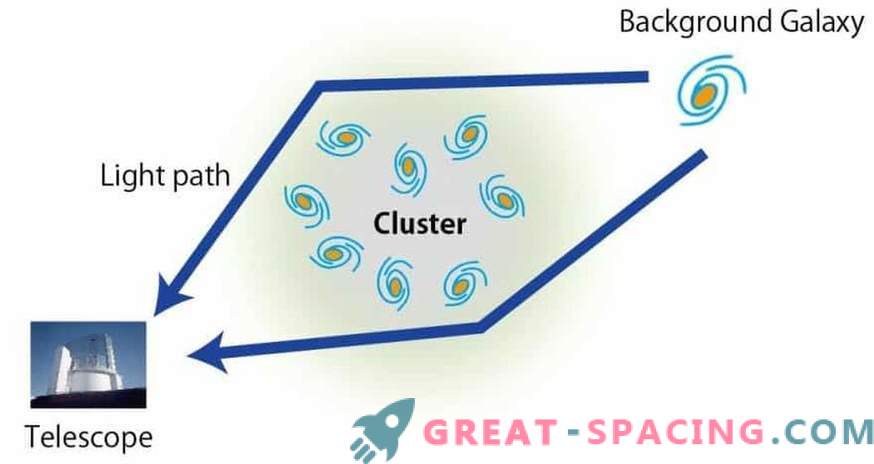
Schematic representation of gravitational lensing. Light rays from a background galaxy are bent by the gravity of a galactic cluster
One of the difficulties of the study was the need for accurate measurements of distortion. To overcome this problem, the group used accurate data from the Hubble Space Telescope and the Subaru telescope. Together with information about the gas temperature from the X-ray satellite, Chandra was able to statically examine these data and find that they comply with a simple law, represented by the magnitude, mass, and temperature index of the gas in the clusters. With the help of computer models it turned out to show that clusters grew by 4-8 billion years according to the law. Theoretically, this law means that large galaxies are still in their teens, continue to grow, pulling a large amount of surrounding matter.
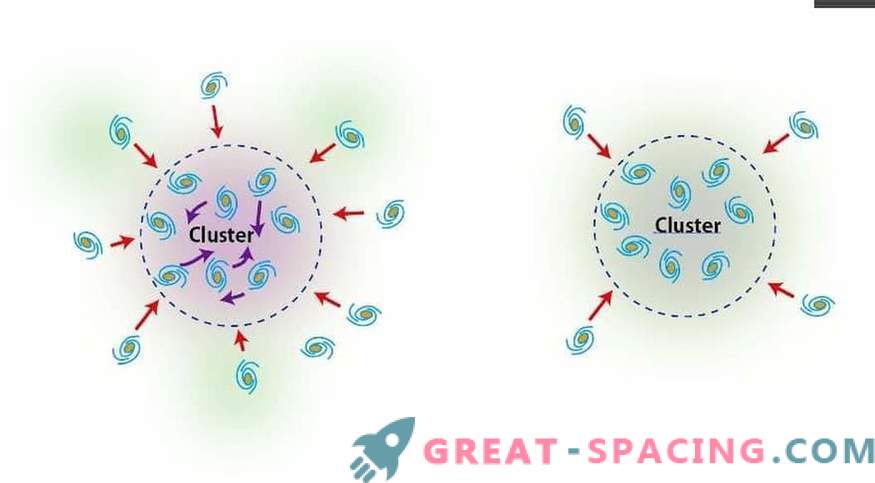
Left: A growing cluster that attracts many galaxies and dark matter. Galaxies are falling rapidly, and the temperature of the gas rises. Right: Developed calm cluster, attracting little matter
The law is so simple that it can be used to calibrate the observed relationships in clusters. This is a key element in the study of the cosmological laws of the universe.