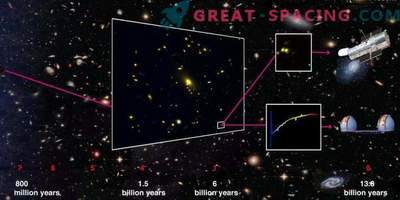
The Galactic Cluster of Abell 2744, distant from us by 3.5 billion light years and containing more than 400 galaxies. The combined gravity of all galaxies causes the cluster to function as a lens through which scientists hope to see the formation of the first stars.
About 200-400 million years after the Big Bang, the first stars appeared. Due to their remoteness, they remain inaccessible to the earth observer, but things can change in 2020 after the launch of the NASA space telescope, James Webb.
The first stars are important for researchers, as they are able to tell valuable information about the properties of the early Universe. It would be possible to understand whether binary stars were common or just singles. And also, how many heavy chemical elements were created by the first generation and how they were formed.
Gravity Magnifying Lens
The first step is based on the infrared sensitivity of the James Webb telescope. The first stars were large, hot and emitted UV rays. But they are so far away that the universal resolution has shifted its peak from UV to much longer IR wavelengths.
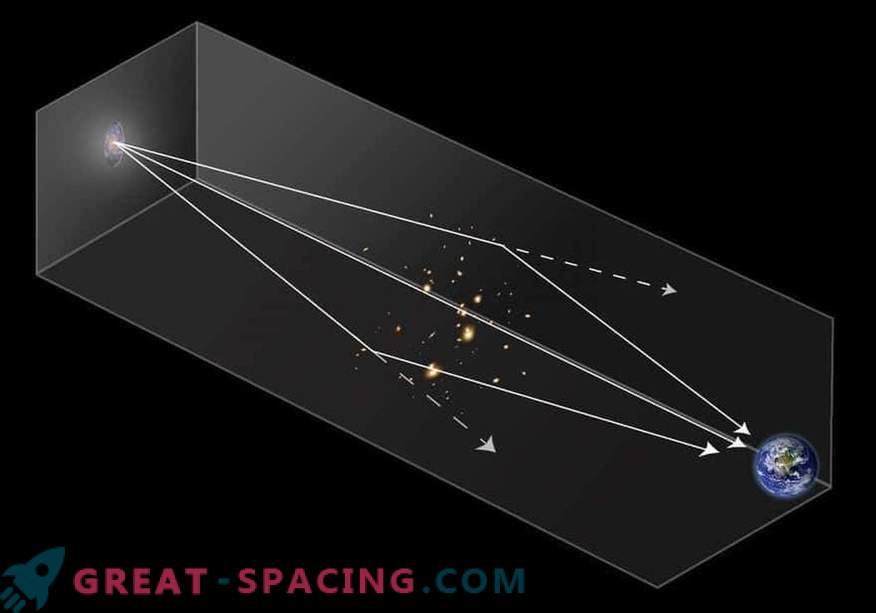
The second step is to use the combined gravity of the intermediate galactic cluster as a lens that will focus and increase the light of the first generation stars. Typical gravitational lensing can increase light by 10–20 times, but this is not enough. For Webb, the increase should be more than 10,000 times. To achieve such an increase, clusters will require transits — special alignments, where the starlight increases significantly over several weeks while the galactic cluster drifts between the Earth and the star.
Good Luck
How likely is this alignment? Astronomers say that the chances are very small. In addition, each caustic is asymmetric, which leads to a sharp increase if the star is approaching on the one hand, but much more vague, if on the other. That is, depending on the side, the star will be brighter for several hours or months. After the peak of brightness, it will disappear again.
The key attribute of the first stars is that they were formed from a mixture of hydrogen and helium of the early Universe without heavy chemical elements, such as carbon, oxygen, iron and gold.
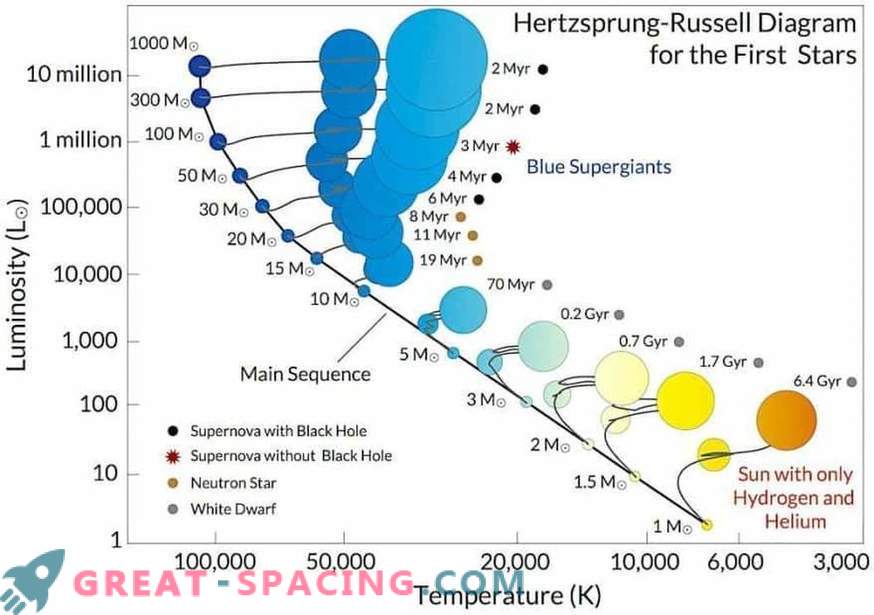
Scientists display stars by temperature and brightness in the diagram. Most are along the main sequence. The sun (below, on the right) has a life expectancy of 6.4 billion years. The first generation is red-hot and grows to a supernova explosion in a few million years
The accretion disk around the primary black holes formed after the Big Bang can become another object seen. Black holes would be the final evolutionary result of the massive first stars. If the stars were in a binary system, then one would become a black hole, fed by gas from the satellite and formed a flat disk. An accretion disk will display a different spectrum from the first star, because it passes through the caustic, creating improved brightness at shorter wavelengths from the hot, innermost part of the disk.
Scientists have already chosen several potential targets, among which is the El Gordo galactic cluster. The team hopes for good luck and long search (all the time, the functioning of James Webb).
Outside of Webb
The James Webb Space Telescope will be a real technical miracle, but it will not last forever. For example, Hubble has been in orbit since 1990 and has been serviced by astronauts 5 times. Webb is planned to be located at a distance of 1.5 million km from Earth, and the term of work was originally calculated for 5-10 years (it can reach up to 15). However, maintenance is not provided.

Therefore, it is planned to create a new telescope on a high and dry top of the Las Campanas Observatory (Chile). This place is ideal for IR surveillance. In 2026, the GMT (Giant Magellan Telescope) will have a light-gathering surface of 24.5 meters, created from 7 individual mirrors. At a certain period, these telescopes will work together, so scientists plan to make the most of all the opportunities to find the first stars.