With a crew of three to six people, there is a lot of work on the International Space Station (ISS), since it cannot function independently. The station depends on regular replenishments from the Earth in the form of food, water, and equipment for astronauts on board — not to mention all scientific experiments.
However, last year three separate programs failed to replenish their reserves. But in general, service programs work on the ISS, flying constantly with people since November 2000. On Wednesday (August 19), the Japanese Space Agency (JAXA) launched its H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV) with a 5-day mission to the ISS.

There are five European automated transmission tools that deliver to orbit. They are able to carry dry cargo (for example, equipment) and bulk cargo (for example, fuel stations) for transfer to the station. A department under pressure, which makes up 90 percent of a cargo carrier, can be accessible to two astronauts for up to eight hours, a time sufficient for unloading. The last ATV left the station in February 2015, and disintegrated in the atmosphere, as planned, loaded with sensors. It is planned to develop a more cargo ship in the future, they say in the ESA.

Cygnus is a spacecraft developed by the private company Orbital Sciences Inc. as part of the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services contract with NASA. The spacecraft made four flights to the international space station since September 2013; the last one was made in October 2014, ended as a result of an explosion due to a problem with the rocket that carried it. The Cygnus design is “borrowed” from other orbiters designed for space flight. For example, the avionics service module, launch and power system previously used in Geostar communications satellites.
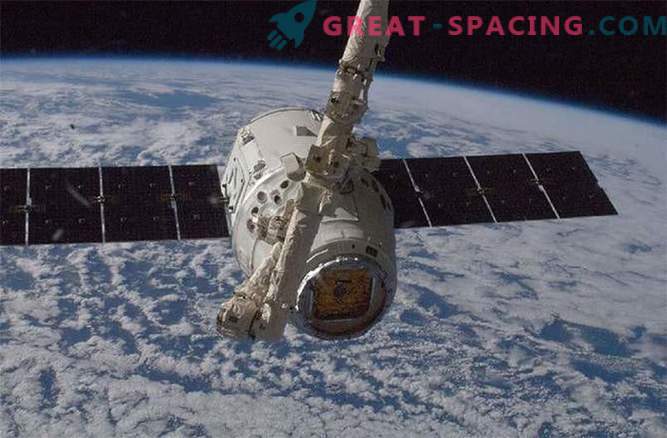

Like Cygnus, Dragon was developed using NASA tools from the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services program. A spacecraft can carry sensitive biological experiments, such as mice or blood samples. The first connection to the space station was in 2012. SpaceX now uses a similar design to create human-controlled spaceships that will fly no earlier than 2017.
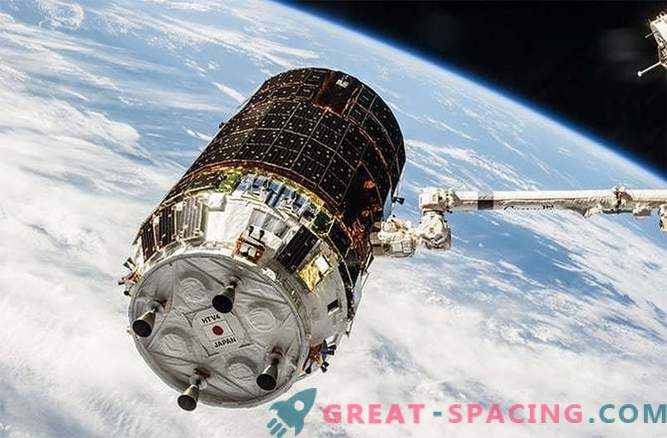

H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV) - also known as Kounatori, which means “white stork” - has now been launched five times to the International Space Station since 2009. The fifth HTV transportation of goods is currently in its initial stages; was launched on Wednesday (August 19) and the ship should arrive at the space station on Monday (August 24).
The spacecraft includes a compressed internal section for the crew or a cargo of experiments and an open tray that carries experiments or spare parts for installation outside the station using the Kibo robotic arm. Although HTV is now the final launch mission under the JAXA agreement, NASA said that agencies will add at least two more HTV flights.
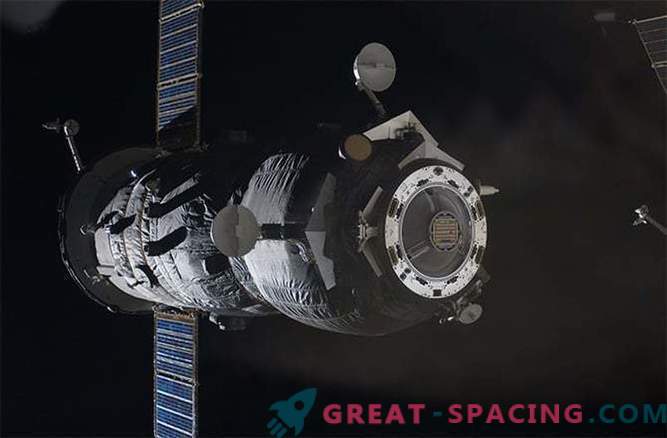

Progress is by far the most durable space station transport ship of all cargo ships. Ship versions have been used in space since 1978. The Progress-M spacecraft made about 60 flights to the ISS, transporting dry cargo as well as fuel for the orbital complex. Progress was lost in 2011 due to a failed launch. In addition, this year, Progress was sent into orbit, but lost control and burned in the Earth's atmosphere.
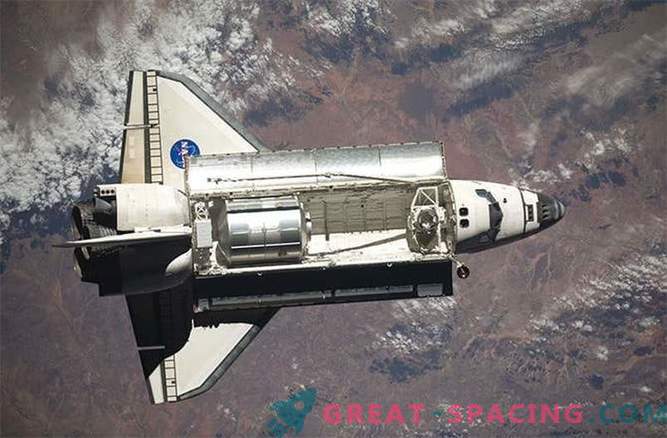

The space shuttle was not only the transporters, it also played a leading role in the construction of the international space station. The crew of up to seven people could be placed in the cabin, without losing space for cargo. Some of the main parts of the station, towed into orbit, include the connecting node (the first part of the United States from the station), the dome of the viewing window, the airlock and the Canadarm-2 robot, which is used to assist astronauts during spacewalks. The transporter was retired in 2011.