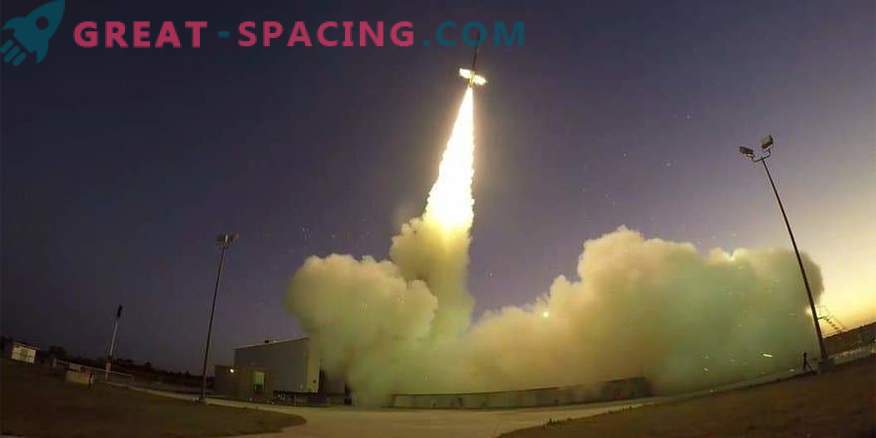
On October 4, the Black Brant IX sound missile system was launched with a length of 17.7 meters. This is the first test of the Mars 2020 mission parachute test.
Experience shows that it is difficult to land a vehicle on Mars and the attempt does not always succeed. Therefore, the ambitious Mars 2020 project will rely on a special parachute, slowing the fall of the spacecraft when entering the Martian atmosphere at a speed of 5.4 km / s. Preparation for the maneuver captured on video.
Mission Mars 2020 will search for hints of ancient Martian life, collecting and analyzing the samples found on the spot. The parachute test series (ASPIRE) began on the basis of Wallops (Virginia). On October 4, they launched the 17.7-meter Black Brant IX sound rocket to evaluate the performance of the ASPIRE payload — an impenetrable cylindrical design with a supersonic parachute, deployment mechanism and computing devices (also high-resolution cameras).
After 42 seconds, the rocket climbed 42 km at a speed 1.8 times higher than sound, providing suitable conditions for the test. A parachute was deployed at this point. 35 minutes after the launch, ASPIRE scattered over the waters of the Atlantic Ocean, 54 km south-east of Wallops Island.
The operation went according to plan, so the next test was scheduled for February 2018.