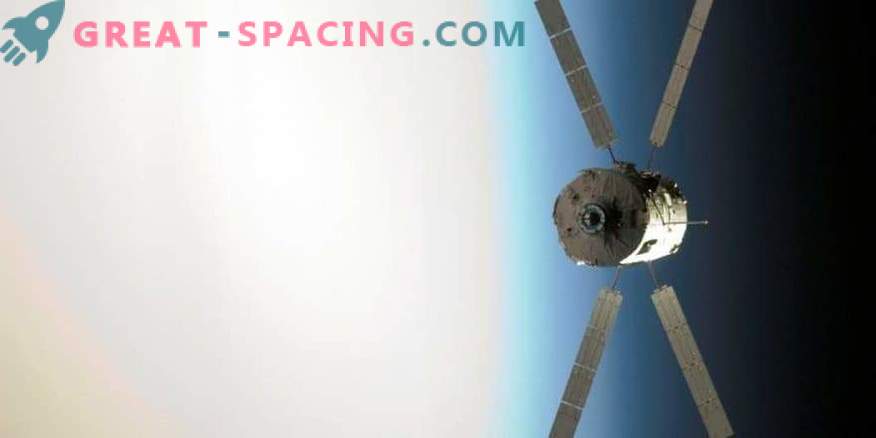
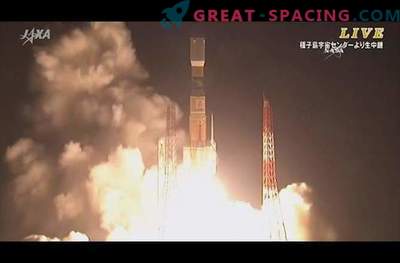
The first ESA automatic vehicle is approaching the ISS against the background of the earth's horizon. The device started on March 9, 2008 and received the name Jules Verne in honor of the 19th century French writer who inspired millions of people for great discoveries.
The task of the device was to demonstrate the safe ability to deliver cargo to the ISS. For this pioneer mission, there were much more demands than previous candidates.
It was launched on the Ariane-5 rocket, after which the device spent 30 days in orbit and docked with the station. During this period, he performed navigation to the ISS and practiced evasion and proximity control maneuvers. On April 3, Jules Verne landed on the ISS and delivered equipment, spare parts, as well as air, food and water to the crew. He remained at the station for 6 months, after which he detached himself and returned to the earth’s atmosphere.
After that, 4 vehicles delivered 6.6 tons of cargo every 17 months. The mechanism also regularly went to a higher orbit in order to overcome the resistance of the earth's atmosphere. In total, model Jules Verne completed 5 successful missions, demonstrating her functionality, European potential and superiority in space exploration.