The 2008 image shows Saturn taken by the Cassini. After 20 years of work, he will plunge into the planet on September 15
It has been 20 years since the launch of Cassini’s mission to Saturn. The whole world is waiting for his final immersion into the atmosphere of a giant. There is no turning back, but NASA hopes to use every second of the pass to get the maximum amount of data.
This is the only ship that went into Saturn orbit. For 5 whole months he studied uncharted territory, passing into the gaps between the rings, completing 22 passes. On Monday, he ran past the Titan for the last time in order to slow down and shift the dive trajectory. It will fall at a speed of 122,000 km / h and melt in a minute.
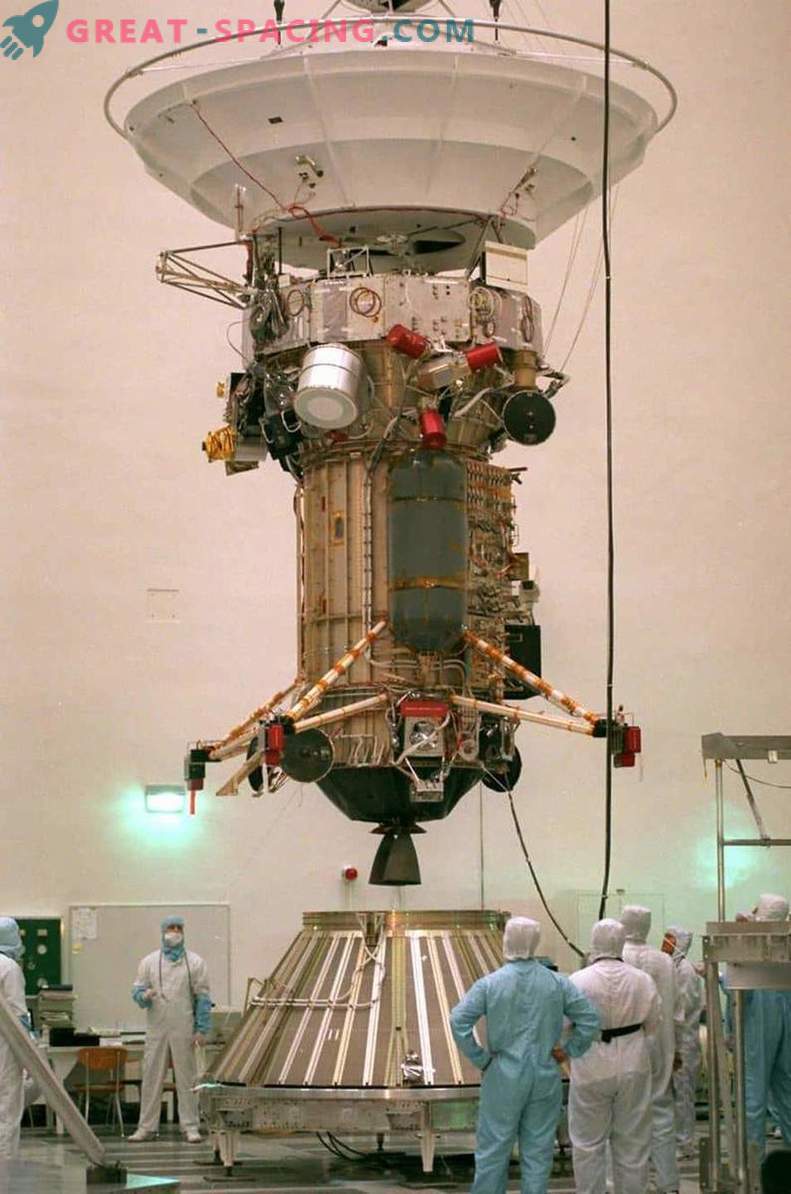

On September 20, 1996, scientists prepared the Cassini apparatus for launch.
This is a wild, innovative and absolutely amazing mission. Earth telescopes will follow this show until the last breath of Cassini at a distance of 1.6 billion km. On board is dangerous plutonium, which, when exploded, will dissipate into the atmosphere. Guide forced to destroy the apparatus, so as not to infect satellites with terrestrial microbes.
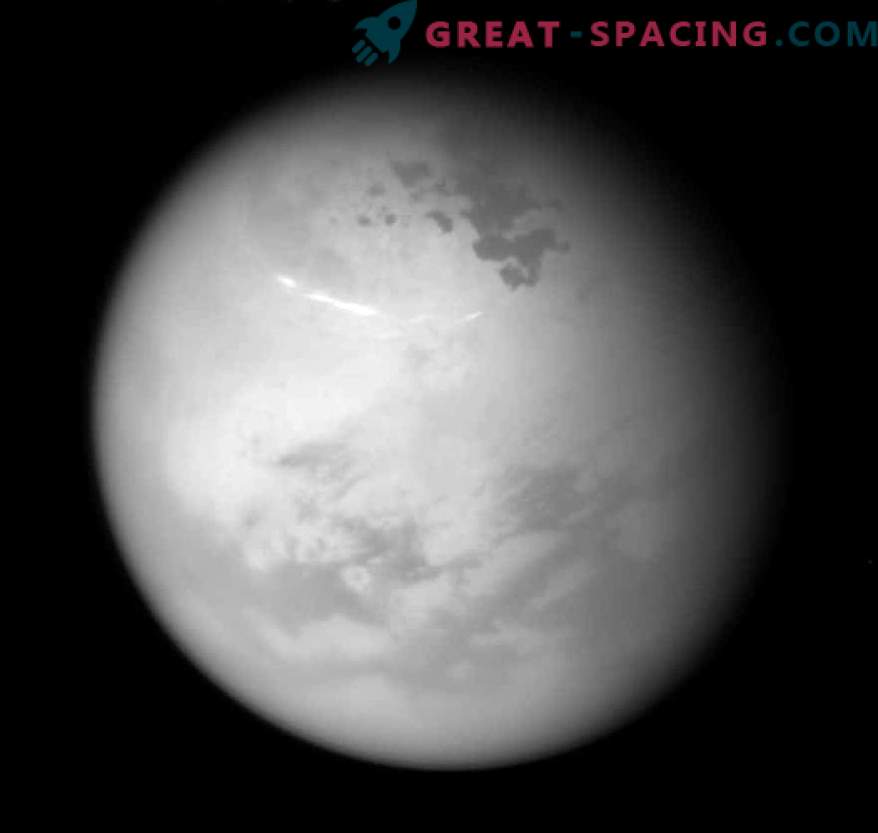

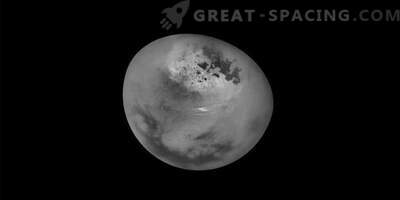
The bright methane clouds on Titan along with hydrocarbon lakes and seas are seen in the 2017 image.
Before Cassini, only three ships flew past the giant: Pioneer 11 (1979), Voyagers 1 and 2 (1980s). But they did not look into orbit. Since the start, Cassini has covered 7.9 billion km, extracted 453,000 images and sent 635 gigabytes of scientific information.
The Huygens apparatus still remains on Titan since landing in 2005. This is still the only mechanism that landed on one of the external objects.

The image of 2017 shows the shadow of the rings. Cassini will transmit atmospheric data during the dive.
The vehicles managed to find seas and lakes from methane and ethane on Titan, and also to detect jets of water vapor on Enceladus. These satellites are potential targets for finding life, so it is important to destroy the ship and not allow it to accidentally break on their surface.