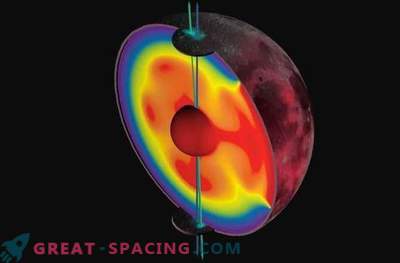
Scientists from the University of Colorado are proposing a new idea of the excessive equatorial bulge of an earth satellite fixed more than 4 billion years ago, when the moon gradually moved away from the planet.
The study sets the parameters for the rapid separation of the moon from the Earth. There is an assumption that the hydrosphere of the nascent planet did not exist or was frozen at that time. This indirectly supports the theory of the weaker Sun, which gave 30% less energy than it does now.
The fossil lunar bulge is able to dispose of the secrets of the early terrestrial evolution, which are not noted anywhere else. The new model captures two time-dependent process. This is the first time when it was possible to establish the boundaries of the timeline for the early lunar recession.
Now the moon is moving away from our planet at a speed of 4 cm per year. It is believed that the recession is the result of the gravitational or tidal interaction of the Earth-Moon system. The same process causes a slowdown of the planetary rotation and an increase in the duration of the day. Scientists believe that the tidal and rotational forces form the moon after its distance, lower the temperature and push it further. It was these effects that slightly flattened the satellite at the poles and made a solid bulge on the lunar crust.
The specific dates and necessary conditions for the formation of the bulge remained unknown. The first of its kind dynamic model helped to determine that the process was not sudden, but slow, and lasted several hundred million years, when the Moon departed from Earth 4 billion years ago.
If the hydrosphere of the planet then existed, then it had to be frozen in order to suspend tidal forces and friction. The snowball hypothesis was proposed for a period of 600 million years ago and was based on geological data. Researchers will continue to develop a model to fill the empty places in the knowledge of the early history of the Moon and the Earth between 3.8-4.5 billion years ago.