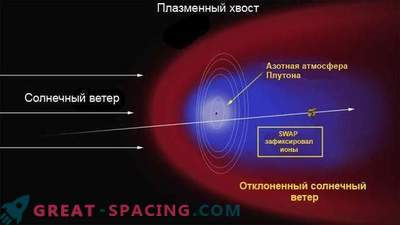
Researchers found that the earth’s atmosphere contains more rare nitrogen molecules than can be explained by geochemical processes carried out near the surface
Scientists used the UCLA instrument and found new data regarding the distribution of the rare nitrogen molecule.
The atmosphere of our planet is different from the atmospheres of most other rocky planets and satellites in the solar system, because it is rich in nitrogen (78%). Titan’s largest satellite also has a nitrogen-rich atmosphere that is somewhat similar to ours.
If we compare nitrogen with other key elements for life, then it wins in terms of stability. Two nitrogen atoms combine to create N2 molecules that linger in the atmospheric layer for millions of years.
The atomic mass of most of the nitrogen is 14. Less than 1% of nitrogen has an additional neutron, which is why nitrogen-15 acts as a rare substance. It is called 15N15N. The researchers measured its amount in the air and found that the rare form of gaseous nitrogen is more numerous than expected. The earth's atmosphere holds 2% more than 15N15N, which can be explained by geochemical processes. Previously, they did not know about the excess, because no one could measure it. Therefore, the UCLA panoramic mass spectrometer made it possible to see it for the first time. This is a unique label for our planet and helps to understand what traces on other planets may look like, especially if they are capable of supporting the life we know.
The study began 4 years ago. To search for 15N15N is difficult, because its atomic mass is 30, which converges with nitrogen oxide. Therefore, the second element suppressed the first in mass spectrometers. The difference between them is only two thousandths of a neutron. But UCLA is able to fix such a slight difference.
Scientists have tested air samples from ground level and to heights of 20 miles, as well as thin air and ocean water. They believe that 15N15N is created due to chemistry in the upper atmosphere, where altitude is close to the ISS orbit.