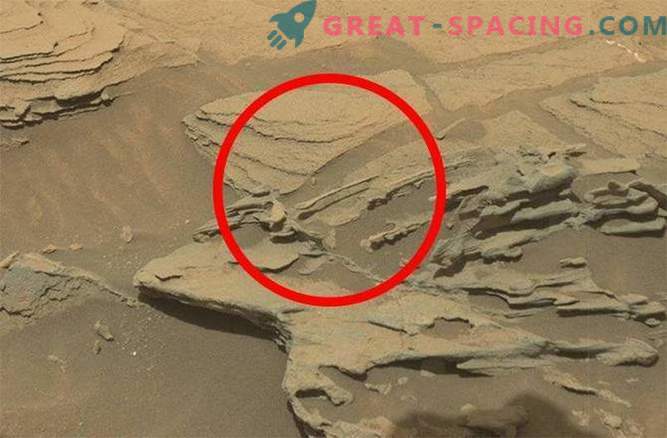
We have already seen “rat”, “yeti”, “face” and even “elephant” on Mars, but this new image made by NASA's Curiosity rover is one of the most fascinating images of rock on Mars.
Of course, this example, like the others, was quoted, but this “spoon” is another excellent example of the effect of pareidolia on Mars, but with its own twist.
This last feature on Mars was spotted by members of the UnmannedSpaceflight.com in an image made by a Curiosity camera called “Mastcam” on August 30th. It really looks like a spoon hovering in the air that extends over some kind of layered rock. But Mars is deprived of any developed civilization capable of constructing this object. This is a logical answer, the truth of it, this feature of the rock does not become less amazing.
Pareidolia is a psychological phenomenon in which our brain interprets a random visual image into an object that is already familiar to us. The most famous example of paradolia is “Person on Mars”, a hill located in the region of Sidonia on Mars, which in the first photo of the Viking spacecraft looked like a face. Now we have high-resolution cameras in Mars orbit, which have shown that this “face” is nothing but the fruit of our fantasy and combination of shadows.
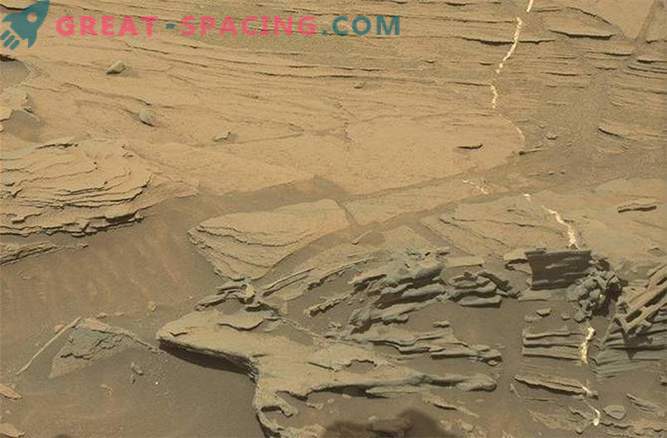

The latest images of Curiosity show stones of all shapes and sizes, which by itself will be the ground for a paradigia and will lead to numerous government conspiracy theories. For example, a rock-like formation not long ago, resembling an iguana, produced an explosion in social resources.
Now we have a “spoon” sticking out of the rocks of Mars. Undoubtedly, this is an excellent example of paradolia, but it is also an understanding that fascinating geological processes are taking place on Mars.
Windy erosion
There are rocks on Earth that have been exposed to wind erosion for hundreds of thousands or even millions of years, which can give an unnatural form of rock formation (for example, the Garden of the Gods in the state of Colorado). But on Mars, where the atmosphere is very thin, weak gravity is present, and other erosion processes are less affected, the wind can create even more elegant structures than on Earth. Eolian processes (windy processes) dominate on Mars and generate everything from small dust tornadoes to real dust storms. This windy activity forms vast dune fields and winding valleys. In addition, thanks to Curiosity's exploration of various rocky outcrops at the foot of Mount Sharp, we know that mineral veins are commonplace. Often, these mineral veins protrude high above the surrounding soft sedimentary rock. These veins have been found to be rich in calcium sulphate and indicate episodic water flows in the distant past of Mars.
And these veins can contribute to the strengthening of small structures, like this “floating spoon”.
This feature is undoubtedly a vivid example of a spoon paradydia. But this amazing find presents some geological hints of erosion processes on the surface of the Red Planet.