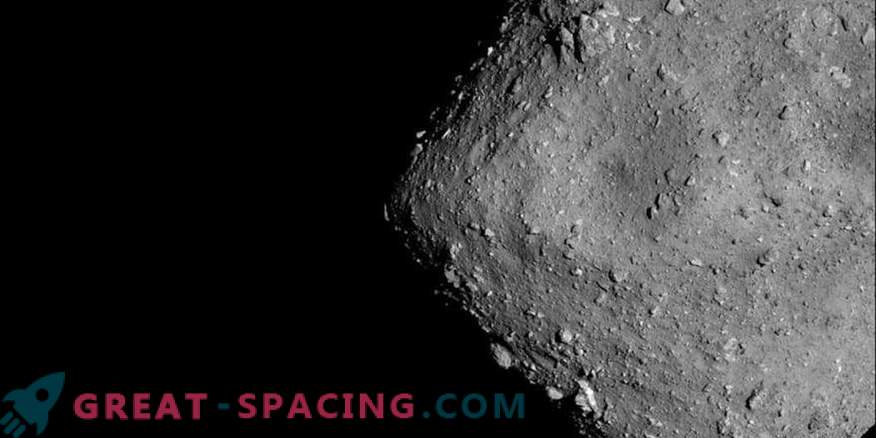
This is not a satellite and not a terrible star of death or some freaky alien mechanism. Before you asteroid! New shots of the asteroid Ryugu from the Japanese probe Hayabusa-2 look slightly frightening, and the object itself resembles the awesome Death Star from Star Wars. But there is no reason to worry.
Hayabusa-2 continues to measure the shape of Ryugu, but preliminary data indicate that the asteroid resembles a rotating vertex. At the very top is a dipole, resembling a tiny hole. For an asteroid is difficult to observe, because you have to track the orbit of a spacecraft. Usually, scientists display the shape of the world by studying the trajectories of an orbital spacecraft, which is attracted to an object in places with increased massiveness. But it is difficult to do this with a small object (900 m).
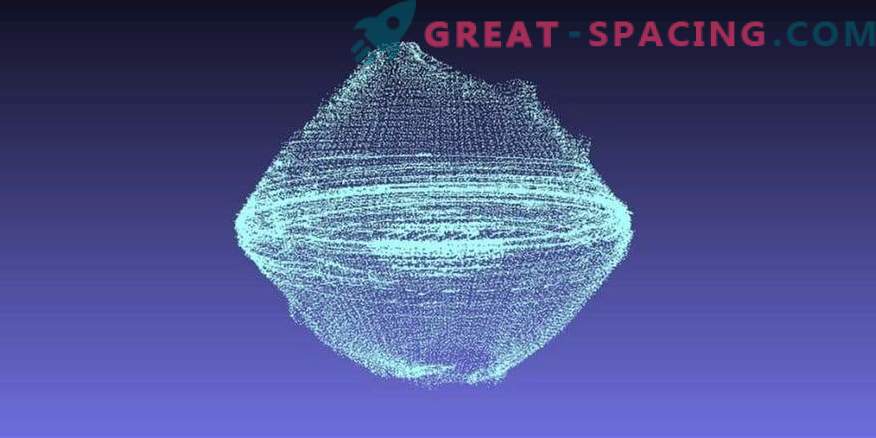
A glance at the asteroid Ryugu extracted by the laser altimeter of the Hayabusa-2 spacecraft after a month of measurements
While the researchers are adjusting the Hayabus-2 trajectory, they are also extracting surface data to prepare for several “landing” procedures to obtain soil and deliver samples to Earth. The probe will also deploy several landing gears and rovers to study the surface layer. Pictures at a distance of 20 km above the surface have already outlined hundreds of rock masses, each of which covers 8-10 m in diameter.
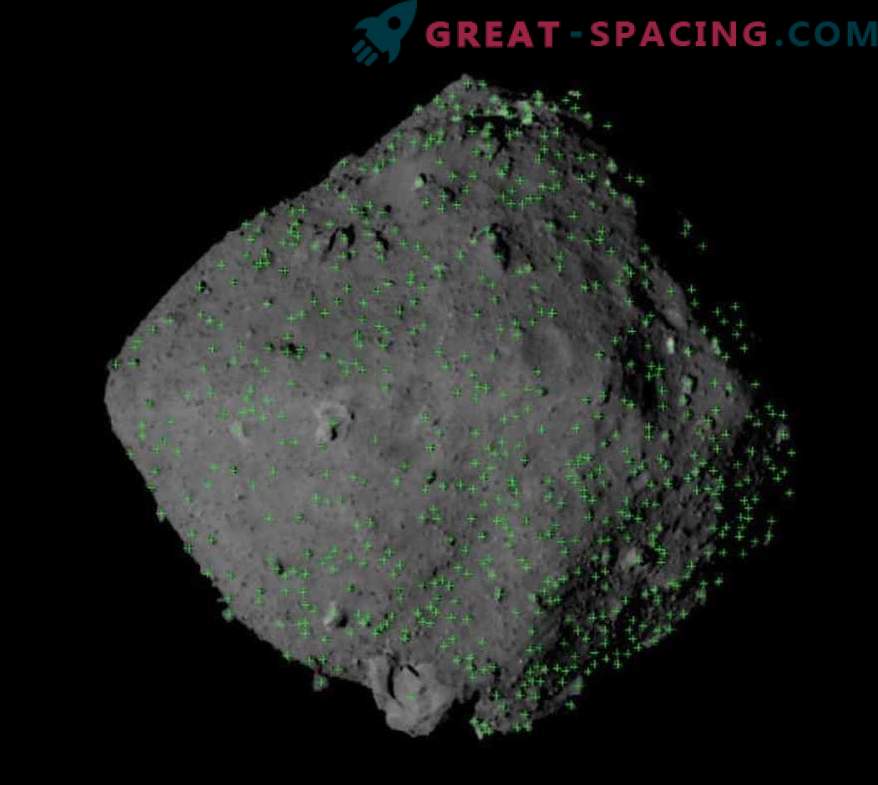

Distribution of rocks on the surface of the asteroid Ryugu - green marks indicate a rock above 8 m
It turned out that there is more rock mass on the surface of the asteroid than previously thought. There are even more stones than on Itokawa (the mission ended in 2010). Scientists are carefully studying the masses to understand the history of the formation of Ryugu. In addition, it is important for researchers to calculate the presence of minerals on the surface. A preliminary map shows the temperature difference on an asteroid in the Hayabus-2 IR camera. A particularly noticeable difference is observed between the northern and southern hemispheres, although the exact cause is not yet clear.
The highest temperatures rise to 100 ° C, and the low reaches the indices of the room space (20-25 ° C). Hayabusa-2 arrived to Ryugu on June 27, and the first landing is scheduled for October.