Astronomers have created an ingenious method of removing the glare of distant stars in order to detect the reflected light of closely rotating exoplanets.
When a hurricane hits the ocean, a peculiar region of calm appears on the water, which is called the “eye of the storm”. Astronomers managed to apply this principle to create such regions of tranquility, but not in the weather, but in observations of star systems.
When scientists try to find worlds that revolve around distant stars, they have the same problem - the starlight hides the reflected light exopalnets that are close to it. Moreover, these highlights in brightness can exceed the reflected light millions of times. This forces astronomers to develop sophisticated methods of dealing with this phenomenon. “Weakeners” are used in measuring devices — most often tiny disks that physically block the intense light of stars in sight (it’s like holding your hand over your eyes to obscure the sun), allowing you to detect the features of a star.
But the “weakeners” have limitations. Although they make it possible to detect the eco-planet at a remote distance from the star, many unidentified objects remain near it. It turns out that whole systems may not be available for our review if their orbits are small.
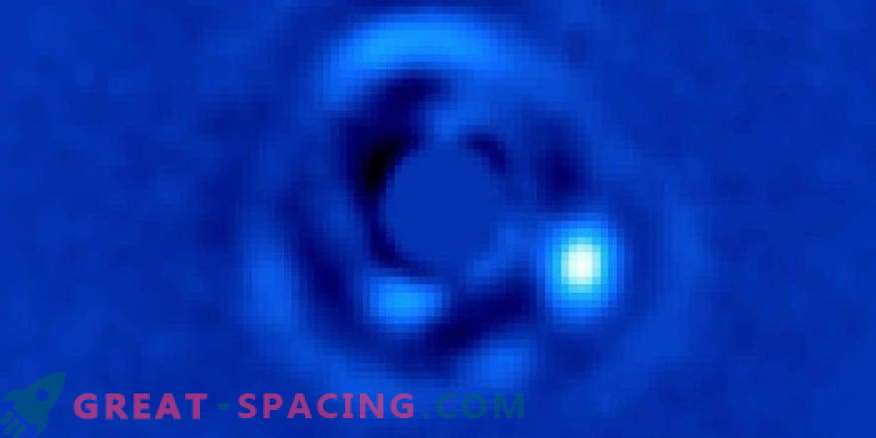
However, the new device, the “vortex coronagraph,” installed at the Keck Observatory in Hawaii, changes the properties of light. He showed the presence of a brown dwarf rotating close to the star HIP 79124 (pictured above) and highlighted the formation of a planetary cloud around the young star HD 141569. They would never have been noticed using familiar methods. “The vortex coronagraph allows you to look into the regions of stars where giant planets are hiding, such as Jupiter and Saturn,” said scientist Dmitry Mavet from the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory. - “Until now, we could only get pictures of objects close to us. And now we consider the planets located close to their parent stars. Their distance is about the same as from Jupiter to the Sun, or two to three times less than previous observations allowed. ”
The vortex coronagraph manipulates the starlight. The filter with microscopic concentric rings acts to direct the bright light of the star from the optics of the instrument. Since light is electromagnetic waves, in the center of the coronagraph these waves cancel each other (in physics, destructive interference). This creates a dark area in the center - the “optical singularity”, which effectively blocks the light of the star.
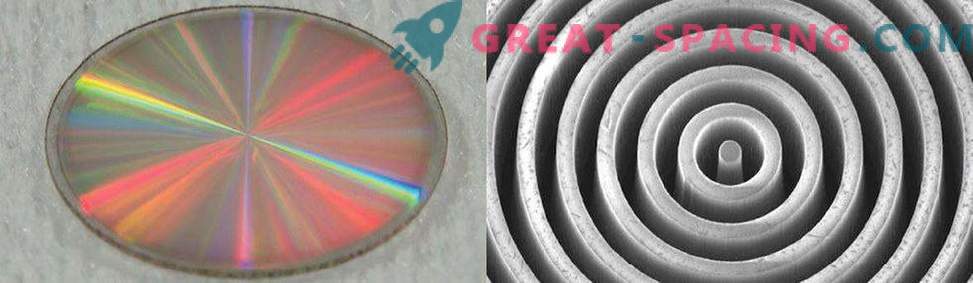
Recalling a miniature CD, the vortex coronagraph mask is made of synthetic diamond. The microscopic view of its concentric rings is shown on the right.
In the case of HIP 79124, the brown dwarf orbit has a total of 23 a. e. (1 a. e - one revolution of the Earth around the Sun). These objects are usually perceived as “failed stars” - they form a bridge between the most massive planets and the least massive stars, and also possess qualities of both.
In another study, the inner ring of the planetary formation around the star HD 141569 was studied. Conclusions suggest that the material consists of silicate pebbles, known as olivine, which is abundant in the Earth's mantle. Its temperature reached about 100 Calvin (280 degrees Fahrenheit). It is a little warmer than the asteroid belt of the solar system.
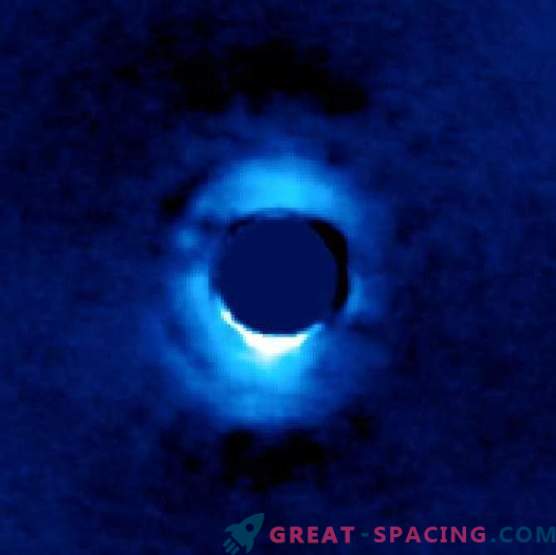

A dusty disk of planetary material surrounding the young star HD 141569, located 380 light years from us.
“The three rings around the young star resemble a matryoshka, each of which passes through changes similar to the formation of planets,” said Mavet. “We noticed that silicate grains have heaped pebbles, which are the construction sides of planetary embryos.”
This mechanism will help astronomers to better understand the formation of worlds around other stars, and this, in turn, will improve our knowledge of our Solar System. In the end, this method will help to make the first direct image of the real Earth.
“The force of the whirlwind allows you to take pictures of the planets located close to the star, which we have not yet been able to do for the Earth,” said Jin Serabian. - “This mechanism will allow for the first time to find the same blue dots in outer space as ours”.